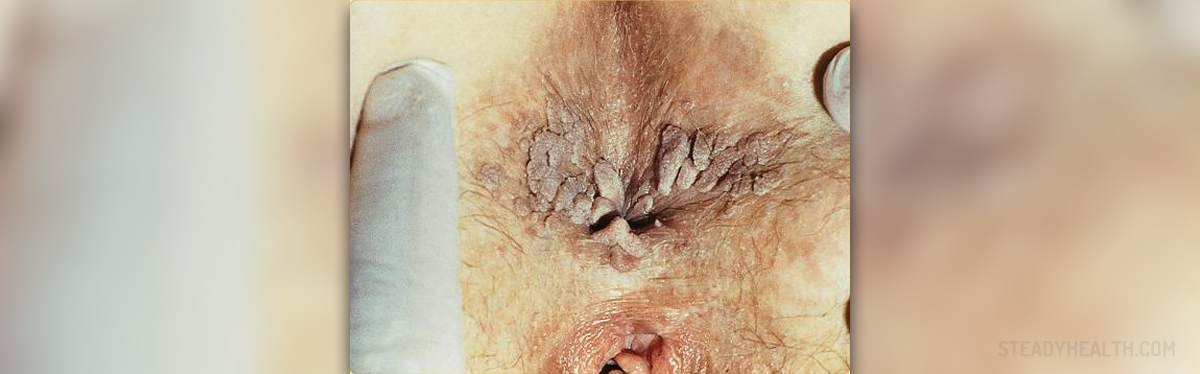
Genital warts or condylomata acuminata are a sexually transmitted disease caused by human papillomavirus or HPV. HPV has many strains, some of them causing cervical cancer and others causing genital warts. Strains 6 and 11 are responsible for 90% of genital warts outbreaks.
Contracting and identifying genital warts
Genital warts can be contracted by having unprotected sex with a person infected with HPV. The period of incubation is one to six months, which means they can appear six months after having sex with an infected person.
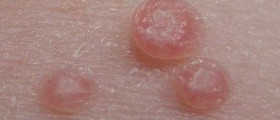
In women, genital warts appear on the vulva, inside the vagina, on the cervix and around the anus, and men usually get them on the penis, the scrotum and around the anus. Genital warts are similar to regular warts, they are small, round and fleshy and sometimes they form clusters that look like cauliflower.
Men and women who suspect they have genital warts should see a doctor who can make a definitive diagnosis based on the tests done with acetic solution and an instrument called colposcope. For women, a Pap spear is usually done to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for genital warts
The problem with genital warts is that the warts themselves can be removed, but not the virus. The virus, however, does not linger in the body forever and it goes away on its own after some time. Still, most doctors recommend removing the warts so they do not grow bigger or more numerous.
Topical treatment for genital warts, which can be done at home, usually consist of using different substances to “burn off” the warts. This type of treatment is only suitable for external warts. There are also topical ointments that are available by prescription. The most commonly used ones are imiquimod, podofilox, trichloroacetic acid or 5-fluorouracil cream.
Sometimes warts need to be removed surgically. Surgical options for wart removal include laser surgery, cryosurgery and electrocautery. Laser surgery is the least painful but it is not very cheap. Cryosurgery uses liquid nitrogen to freeze the warts off while electrocautery uses electric current that burns the wart.
Another option is injecting Interferon alpha, which is an anti-viral drug, but it is only effective in 50 percent of the cases and sometimes requires a second dose.
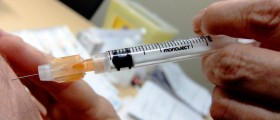
Finally, immunization for women is now available in form of a vaccine against several common strains of HPV, including those that cause cervical cancer and those that cause warts. Health authorities recommend these vaccines to all girls between ages 11 and 26. It comes in three shots over a six-month period.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...