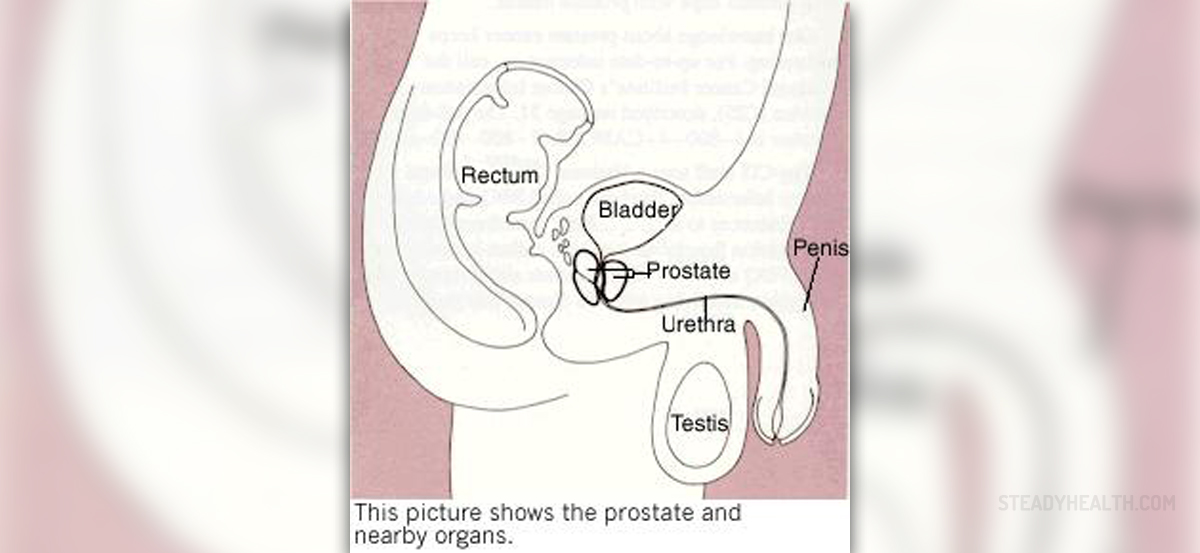
The prostate is a gland located below the bladder and around the urethra. Its function is to produce one of liquid components of the semen known as ejaculatory fluid. Most men suffering from prostate problems experience first symptoms in their 50s. One of common problems is non-cancerous (or non-malignant) enlargement of the prostate called benign prostatic hyperplasia or simply BPH.
About BPH
Benign prostatic hyperplasia usually starts several decades before it shows first symptoms, and doctors are able to identify the beginning of this condition even in men in their 30s. However, most people do not have any symptoms whatsoever until they turn 50. This condition is very common and affects about 50% of elderly men, but just some 10% of them need specific medical assistance.
This condition is characterized by the growth of the prostate gland, which may result in several medical problems. Common problems are compression of the urethra, obstruction of urine flow and urine retention. Frequent urination and frequent urge to urinate (especially at night) are also troubling many BPH patients, as well as problems with initiation of urination and slow urination. Situation may gets worse and patients may suffer from frequent urinary infections. Additional complication is complete blockage of the urethra, which requires urgent medical assistance.
BPH is not a type or forerunner of prostate cancer. This change in prostate size is completely benign. The doctor (urologist) detects enlargement of the prostate during a digital rectal exam or cystoscopy exam of the urethra, prostate and the bladder.Prevention of BPH
Regular medical checkups and prostate exams are the best way to prevent prostate problems, including benign prostatic hyperplasia. Make sure to visit your doctor if you experience any of the symptoms characteristic for BPH. Frequent urge to urinate, urine dribbling or problems with urination should be reported to your doctor as soon as possible, to avoid other potential health complications.
Even if you have had BPH surgery, you should still check your prostate regularly. BPH treatment does not protect you against prostate cancer, so you must look after your health.
BPH Treatment Options
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is treated only in men with severe symptoms and treatment may include medications or surgical procedures. Common BPH drugs are alpha blockers such as tamsulosin, terazosin, doxazosin or alfuzosin, or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (dutasteride or finasteride).
Different surgical methods are also available for BPH patients, especially for those unresponsive to drugs or with serious medical problems. Laser procedures, transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and microwave therapy are some of surgical options for benign prostatic hyperplasia.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...