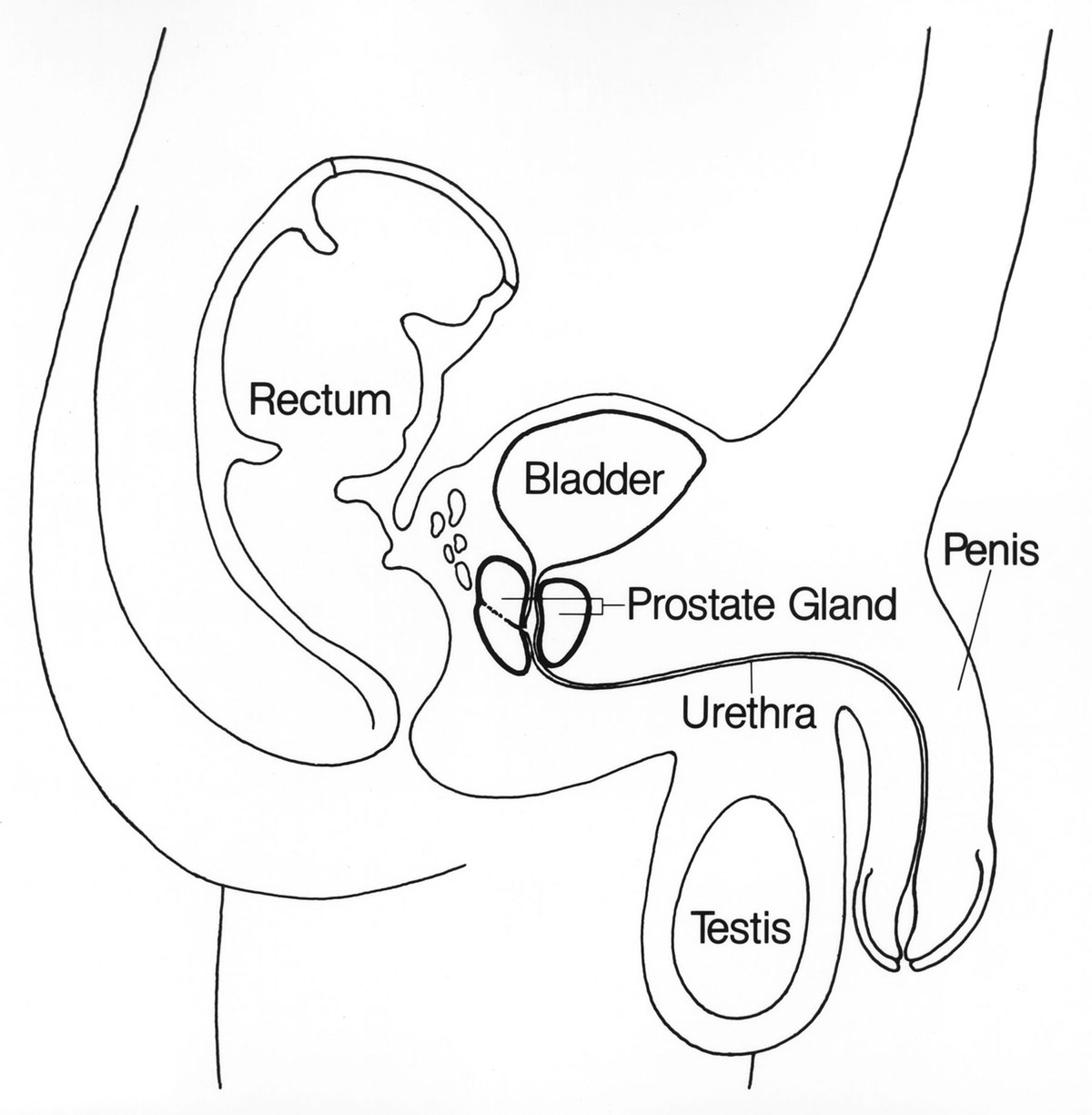
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is benign enlargement of the male gland which is situated in pelvis right above the bladder. Enlargement of this gland is so typical for the men in sixties and seventies. Placed between the ureters and the bladder this gland is primarily in charge with carrying the urine. As for other roles it secretes alkaline fluid which is a part of the semen and with its muscles it helps in ejaculation. In case of the enlargement of the gland it constricts the urethra making it difficult for a person to urinate. In extreme cases a person cannot urinate at all which is an urgent state.
The benign prostatic hypertrophy may be treated surgically. This is the most efficient and permanent way of treating the condition. The symptoms may be postponed for at least 10 years after the surgery. The complications of the surgery are minimal and include erectile dysfunction.
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is the most conducted type of surgery. It is done under spinal anesthesia. This is the gold standard of treating the disease. The very surgery includes insertion of a tinny tubular camera or endoscope through the urethra into the bladder and excision of the excessive prostate tissue. In the same act the urologist examines the bladder for possible presence of stones or even bladder tumors. In case everything is in order the electrical loop is placed up through the urethra near the area where prostate tissue is pressing the urethra. The loop removes the extra tissue in the prostate and is also used in prevention of over bleeding during the procedure. The tissue that has been removed is then patohystologically examined. This is done to rule out the presence of prostate cancer. Within the healing period patient is inserted urinal catheter to ease the process of urination. The catheter it is removed within the hours after the surgery or a few days later. If patient is discharged with the catheter it will be removed during the following check up at the urologist. There is normally blood present in the urine so patients are advised not to panic. But in case the urine tends to be of intensive red color the doctor must be contacted immediately. Bed rest and drinking a lot of fluid are essential for proper healing. The water will wash out the remnant blood and prevent formation of a clot. Excessive strain and lifting heavy objects are forbidden as well as driving. In case of constipation the doctor may prescribe certain medications and give advice on the dietary regimes.
In postoperative period a person may feel slight urinary discomfort. At first the flow of the urine might be very strong and one may feel unable to control it. Eventually in a few months this will stabilize. The complications of the procedure include ejaculation difficulties which may affect those men who are still eager to have children. The most serious possible complications are erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence.
Extremely rarely the condition is treated with open prostatectomy, the removal of the entire prostate. This method is conducted in case of huge enlargement of the gland and if there are stones present in the bladder.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...