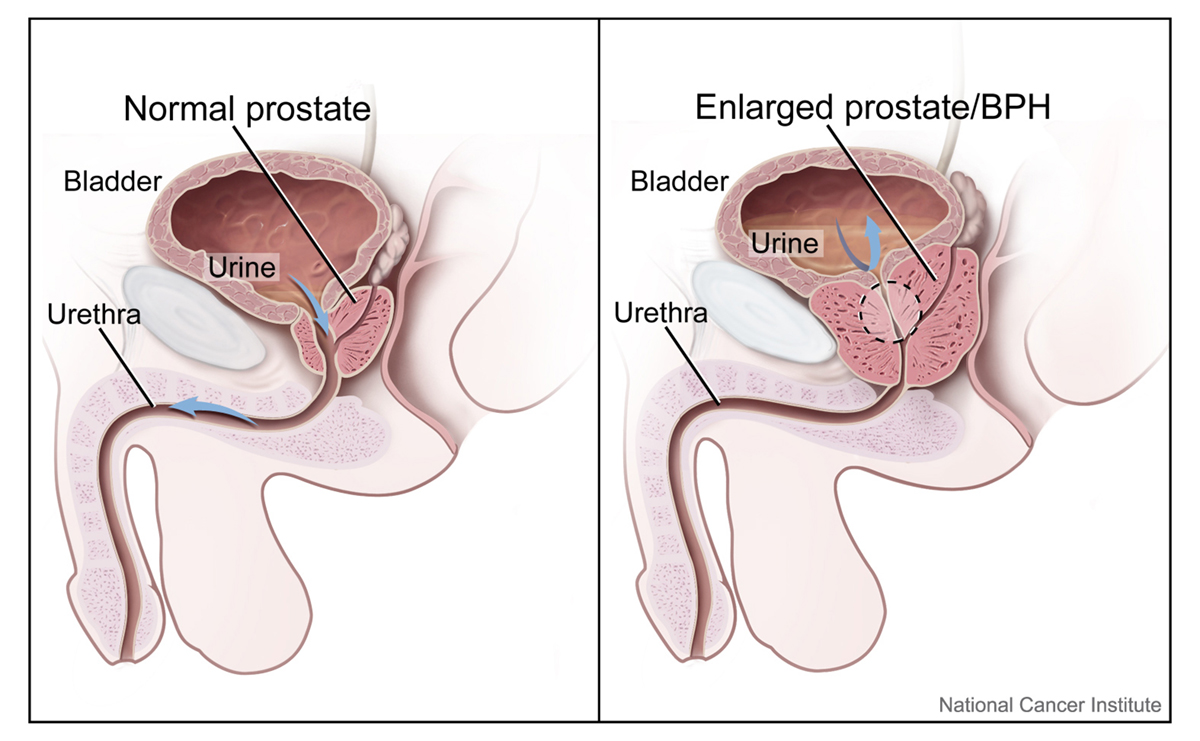
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also known as the benign prostatic hyperthrophy or benign prostatic obstruction is a condition where the prostate gland is enlarged. The prostate gland is walnut-sized gland, located between the bladder and the urethra. The prostate is a part of the male reproductive system. One of its functions is to produce the semen. Bening prostatic hyperplasia commonly occurs as men age and approximately 4 in 10 men over the age of 65 suffer from the condition.
Symptoms of Enlarged ProstateAs the prostate gland becomes bigger it blocks the flow of urine because it presses on the urethra. Affected men usually experience difficulty in starting the urine flow. Interrupted and weak urine flow is also common. Also, men with enlarged prostate have frequent need to empty the bladder and experience dribbling before and after urination.
Diagnosis of Enlarged ProstateIf a doctor suspects enlarged prostate, he or she may perform physical examination to check if the bladder is over-filled with urine indicating chronic urinary retention. To rule out other conditions a doctor may order urinalysis to look for signs of infection. Digital rectal examination is performed to observe the size and consistency of the prostate gland. In this procedure, the doctor puts lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to feel the prostate. Blood tests may also be done to evaluate functioning of the kidneys. Other tests that may help in making diagnosis are: urine flow test, rectal ultrasound, and urodynamic measurements. An ultrasound exam to check if there is urine left in the bladder can help to determine degree of the bladder obstruction. The doctor may also order a blood test to check the amount of prostate-specific antigen (PSA). PSA is a protein produced by the prostate and it is commonly released in the blood stream in BPH. High levels of PSA can be a sign of prostate cancer, enlarged prostate and inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis).
Treatment of Enlarged ProstateIf there is a slightly enlarged prostate, the treatment is not necessary. However, the condition requires careful monitoring and watchful waiting. The patient is at point advised to make some lifestyle changes to relieve the symptoms. That includes limiting alcohol intake, restricting caffeine and learning certain techniques to increase the amount of urine your bladder can hold. If the condition gets worse, there are another treatment options. Medications given for the treatment of enlarged prostate include alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. Surgical treatment is necessary only if a patient didn’t respond to medicines. There are different procedures that may be used. They include transurethral resection of the prostate, transurethral incision of the prostate, open prostatectomy and minimally invasive surgical treatment.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...