
People who have been affected by bronchitis, asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) usually suffer from phlegm in lungs as a result. Phlegm must be expelled from the lungs in order to avoid serious complications such as difficulty breathing and clogging of the airways.
What is Phlegm?
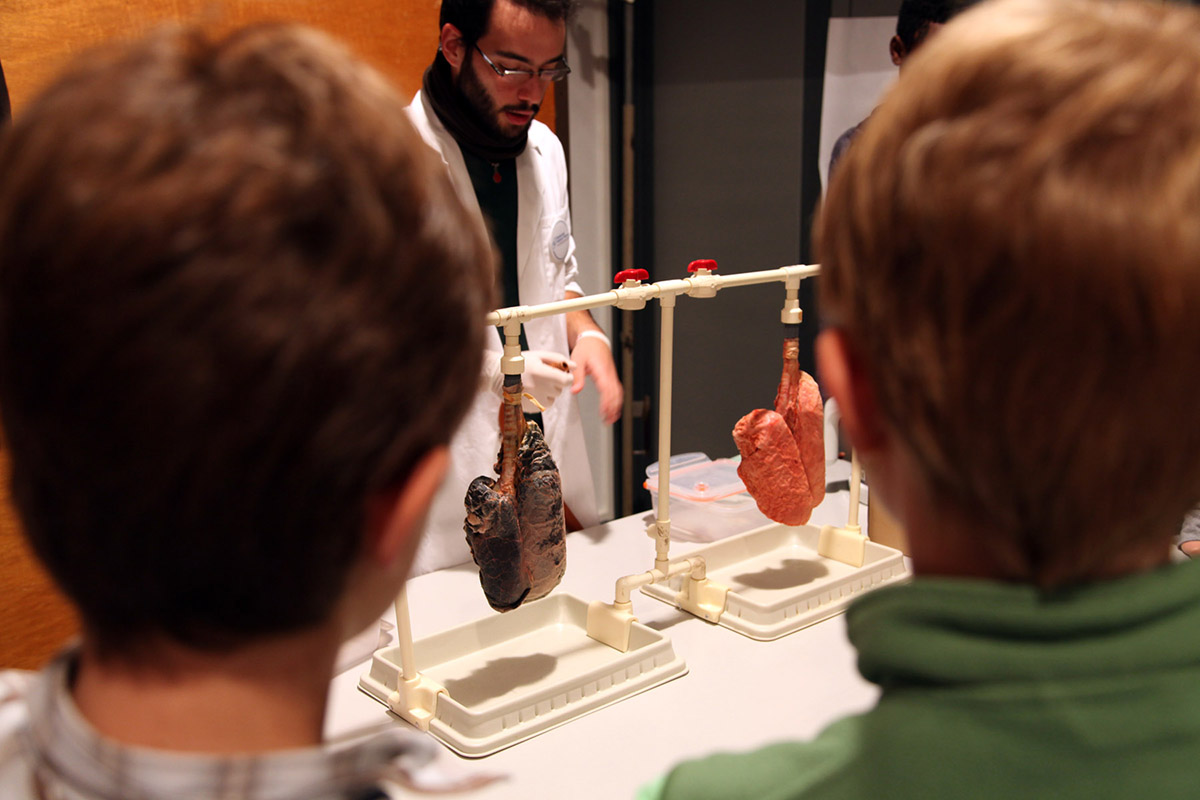
Phlegm is sticky, stringy and thick mucus that develops within the lungs. It is produced by mucus membrane that lines the bronchial passages of the lungs. The phlegm performs important functions such as trapping and filtering allergens and other harmful particles out of the lungs and prevents infections. Lack of treatment for phlegm in lungs may lead to infection and worsening of the problem due to accumulation of phlegm in lungs.
Causes of Phlegm in Lungs
Diseases of different severity can cause phlegm in lungs. The phlegm may develop due to common cold, sinusitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis and other medical conditions. Cigarette smoking can also cause phlegm in lungs due to irritation of the lungs. Other foreign substances too can cause excess phlegm production by the mucus membrane. Prompt treatment of these underlying causes of phlegm is essential in order to prevent irritation of the bronchial tubes. Otherwise, due to delicate nature of the bronchial tubes, it may result in secondary infections.
How to Eliminate Phlegm in Lungs?
There are different measures one can take to prevent build up of excess phlegm in lungs. It is important to avoid cigarette smoking as well as passive smoking and exposure to dust and other environmental pollutants. Affected individuals must also keep themselves well hydrated by drinking 8 to 10 glasses of water per day. Over-the-counter saline nasal sprays help to thin the phlegm. Steam inhalation helps to make phlegm loose and reduce congestion. The cough medicines should be used moderately as they can dry out the lungs and nasal passages and make the phlegm thicker.
Instructions for Expelling Phlegm from LungsTake a chair and sit in upright position with your head slightly forward and breathe normallyAs you tilt your head back, slowly take a deep breathHold your breath for up to four seconds while your head is backThen lean forward and lose the phlegm by coughingUse small short coughs but do not inhale between the coughsTake a pause for few seconds while breathing slowly and then repeat the process for three timesDo not breathe deeply as it prevents removal of the phlegm and causes it to return back into the lungs
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...