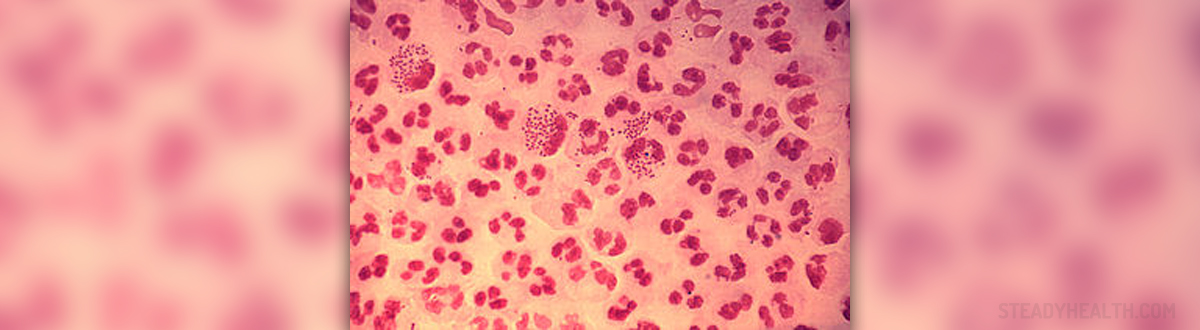
Nongonococcal urethritis, which is abbreviated as NGU, is the medical term for the urethra infection induced by the pathogens that are not gonorrhea. There are various types of pathogens that cause this infection, but Chlamydia is the bacterium that leads to the occurrence of nongonococcal urethritis in the majority of cases. By the way, the infection caused by Chlamydia is much more serious than when the infections is induced by some other germs. Although nongonococcal urethritis may appear in women, as well as in men, it is mostly diagnosed in the males.
Causes of nongonococcal urtehritis
One can get this infection in several ways, but in most cases, one gets infected through the sexual intercourse with the infected person. Furthermore, nongonococcal urethritis may be caused by several conditions, such as urinary tract infection, urethral stricture and catheterization. Moreover, bacterial prostrates can lead to the occurrence of this type of infection. Sometimes it also happens that during birth, the baby is exposed to the pathogens that cause nongonococcal urethritis, and as a consequence, the baby may have conjunctivitis, ear infection or pneumonia.
Symptoms of nongonococcal urethritis
The most common symptoms of this infection in men are penis discharge and burning sensation, as well as pain during urination. Furthermore, the men with this urethral infection may experience uncomfortable itching, irritation and underwear stain.
On the other side, the most typical symptoms of nongonococcal urethritis in women are vaginal discharge, painful urination and burning when urinating. Furthermore, vaginal bleeding, as well as lower abdominal pain, may also appear as the result of this infection. When these two symptoms occur, they are the signs that this infection is developed into a pelvic inflammatory disease.
Nongonococcal urethritis may cause several anal and oral symptoms. For example, one with this infection may experience pain or itching during bowel movements, while the most common oral symptom of this infection is sore throat.
Treatment of nongonoxcoccal urethritis
Once this infection is diagnosed, a treatment should be carried out promptly. In most cases, the doctors prescribe the antibiotics called azithromycin and doxycycline or, in some cases, erythromycin and ofloxacin. If a pregnant woman gets infected, she should inform the doctor about it in order to receive the treatment which is not harmful for the baby. Furthermore, the infected person should abstain from the sexual relations until he/she is completely cured and inform the partner about the infection.
- www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Non_specific_urethritis/Pages/Prevention-OLD.aspx
- www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/urethritis-and-cervicitis.htm
- Photo courtesy of CDC/ Joe Millar by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gonococcal_urethritis_PHIL_4085_lores.jpg















Your thoughts on this
Loading...