What is Diverticulitis
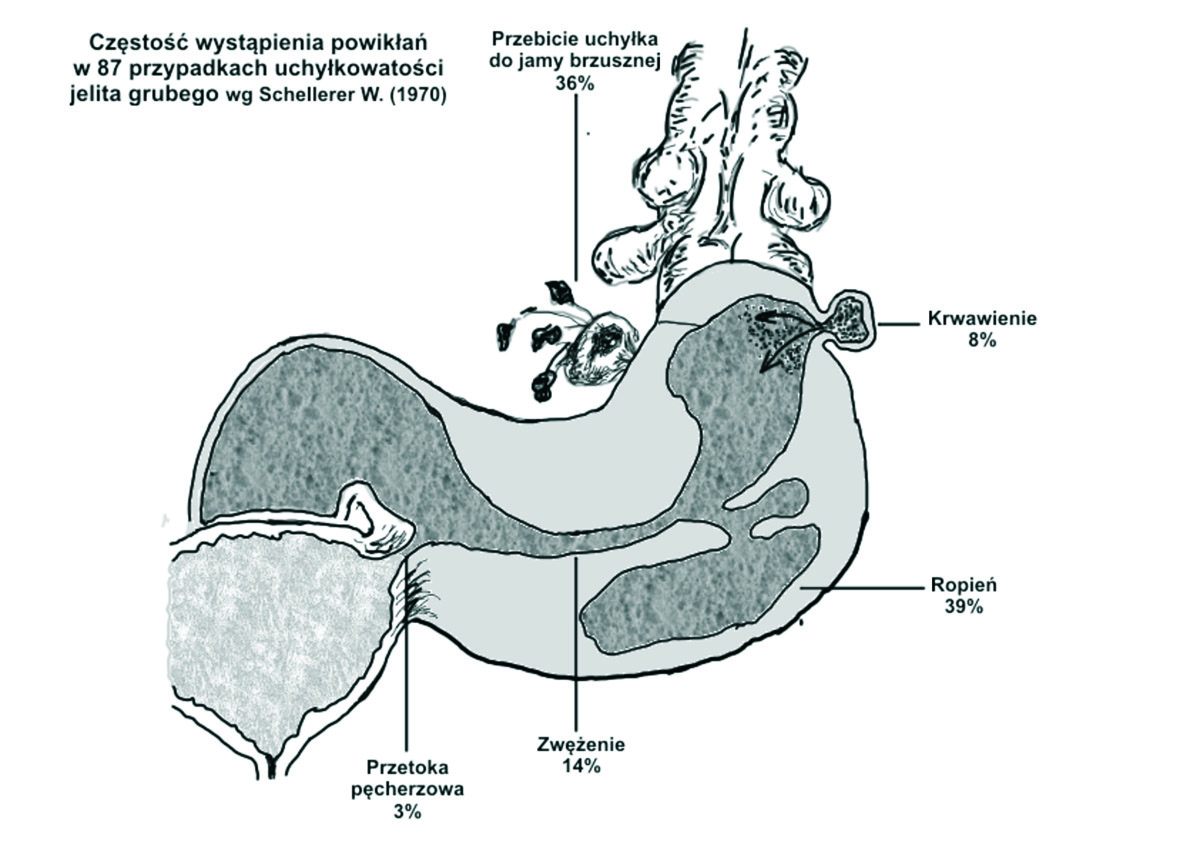
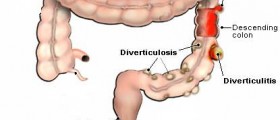
Diverticulitis is an infection caused by the accumulation of bowel contents in small pockets, which are formed in the large intestine. Diverticulosis is formed in about 40% of people after the age of 50. It is a result of diet poor in fiber, impaired bowel or excessive strain during the discharge. Usually, this expansions does not cause any problems, but, it may happen that accumulated content cause pain, hemorrhage and inflammation. If the inflammation expands it causes nausea, vomiting, fever and even shooting when surgical intervention is essential.
There are several herbs that are proven to be very effective in treating this problem.
Psyllium appears in the form of seed husks that contain soluble fiber. This plant uses for decades by traditional doctors and medical professionals for treatment of constipation and diverticulosis. Psyllium husks should be gradually introduced in the regular diet as it can cause gas, diarrhea, flatulence and even allergic reactions. Psyllium can be used in the form of regular or ground husks or in the form of capsules.
Peppermint has multiple positive effects on alleviating this problem. This plant has anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal and spasmolytic properties by which remove pain. Peppermint can be applied orally in the form of film-coated capsules (1-2 capsules 2-3 times a day). These capsules contain peppermint oil which is released in the intestine bypassing the stomach. Also, peppermint oil, mixing with sesame, olive or almond oil, rubs topically on the painful stomach area.
Aloe Vera in the interior of its leaves contain a gel which is most appreciated because of heeling properties in the treatment of sunburn. However, a quite number of medical experts recommend this plant for relieving many gastrointestinal troubles, including the diverticulosis. Aloe Vera can be used in the form of capsules (2-8 capsules daily) or as reconstructed juice (1/4-1/2 cup of juice 4 times a day).
Cat’s claw has many benefits for human health. It uses for centuries in folk medicine of South African area for treating infections, arthritis and intestinal disorders, including diverticulitis. Although there are numerous informal Testimonies about the efficiency of this plant, it was never officially confirmed. Typical doses of this herb are: 20-30 mg extracts daily or 3 cups of tea from the root bark. Since the Cat’s claw lowers blood pressure and can jeopardize fertility, its use is not recommended in pregnancy.
Wild Yam has been known in medicine as a base for the production of hormones (progesterone). In the raw state, this plant has little hormonal values, but, due to spasmolytic properties it uses to relieve pain in the intestines. It is usually used in the form of tincture (1-2 drops 3-4 times a day) in capsule form (1-2 capsules daily) or in the form of tablets of powdered root (3 times a day).
In traditional Japanese herbal (Kampo) medicine, daiobotanpito (DBT) or Da Huang Mu Dan Tang in Chinese has been used in medical treatment of acute diverticulitis for many years based on the experience. Our aim was to investigate whether the treatment of acute diverticulitis can be treated with intravenous antibiotics plus orally administrated DBT than intravenous antibiotics alone. A retrospective nonrandomized open-label trial was established to compare patients with acute diverticulitis who received oral DBT associated with intravenous antibiotics with those who received intravenous antibiotic alone. We included 34 patients, eleven patients in group 1 with DBT and 23 patients in group 2 without DBT.
- A trend toward a day shorter mean hospital stay and fasting was seen in group 1, although this did not reach statistical significance.
- In all cases, CT scan showed bowel wall thickness with different degrees of pericolic fat infiltration and the presence of diverticula. The two groups were comparable with respect to age, sex, previous diagnosis of diverticulosis, previous episodes of diverticulitis, duration of symptoms before admission, and CRP/WBC at admission.
- There was a significantly better outcome in the group treated with DBT than in the group without DBT when comparing duration of fever, abdominal pain, and antibiotics administration.
- There was no adverse effect with antibiotics and DBT in both groups. There was complete resolution of symptoms in both groups.
Diverticulitis Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of diverticulosis in the intestine, it is necessary to change the diet. This implies an increased intake of whole grains, legumes, crunchy vegetables and fruit with a membrane. However, diverticulitis can’t stand insoluble fibers such as nuts, corn, cucumber, tomato, etc. These fibers tend to accumulate in formed pockets which can be very irritating. Soluble fiber mixed with water form a gel which has a small probability to bend in intestinal pockets, so their use (oat, flax seed, peeled apple, gelatin, etc) should be increased.
In addition, problems caused by diverticulitis can be deteriorated by poor digestion induced inadequate chewing of food. That's why some people supplement their diet with digestive enzymes such as bromelain and papain. Caffeine and alcohol can also affect the worsening of symptoms of diverticulitis.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...