About Diverticulum
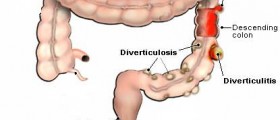
Diverticulum is just one sac or bulge that appears in the last part of the large left intestine, also known as the sigmoid colon, and it occurs as the result of the bulging out of the inner layer through the outer layer of the colon.
Diverticula refer to several sacs. Diverticulosis means the presence of the diverticula in the intestine, while diverticulitis is the medical term for the inflammation or infection in one or more diverticula. This disorder is more frequent in men than in women and usually appears in persons older than 50 years.

Causes and Symptoms of Diverticulitis
The main causes of this disorder are the excessively strong contractions of the muscular wall of the large intestine, a hard diet that leads to the significant narrowing of the colon, and bacteria that is stuck in the diverticula. The most common symptoms of this condition are low abdomen pain, fever, and rectal bleeding, as well as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal spasms.
Homeopathic Remedies for Diverticulitis
Some researchers or doctors state that this disease is an acquired disease and occurs as the result of consuming foods not rich in fiber, which is very important for the normal functioning of the colon. Fiber helps the colon by reducing the tension and expanding once the waste is eliminated. Therefore, one of the recommendations is to enrich the diet with fiber.
Foods, such as whole-grain bread, berries, bananas, peaches, vegetarian meals, and vegetable soup with barley have much fiber. When the fruit is taken, it is better to eat it with the skin. It is also believed that bran fiber is the most effective in preventing and treating diverticulitis.
Sometimes, it is very difficult to accustom the body to receive so much fiber, and in that case, some supplements are advisable, such as psyllium seed supplements. If a person suffers from diverticulitis, drinking a lot of water is very effective and beneficial.
Furthermore, it is crucial not to suppress the need to move the bowels in the case of diverticulitis. Moreover, physical exercises can help in toning the muscles of the colon and therefore, they are also highly recommended.
Suppositories should be avoided and instead of them prunes, prune juice, and herbal teas are very effective natural laxatives. People who suffer from diverticulitis should not smoke or drink much coffee and alcohol, because that can only worsen the condition.
The doctors suggest the patients avoid nuts, seeds, and corn. In order to lessen the pain in the abdominal area, which is caused by muscle spasms, acupuncture is the best solution.
- The cause of diverticular disease is unknown, but several factors may contribute to changes in the wall of the colon, including aging, the movement of waste through the colon, changes in intestinal pressure, a low fiber diet, and physical abnormalities.
- To help prevent diverticular disease: (1) Eat a high-fiber (25 to 35 g per day), low-fat diet that contains lots of vegetables. This diet is also beneficial for overall health, and may reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer. (2) Avoid red meat. (3) Avoid foods that may block the opening of a diverticulum and lead to inflammation, such as high-fat foods. (4) Exercise regularly. One study found that men and women who run have a lower risk of diverticular disease than those who do not run.
- Nutrition plays an important role in preventing and treating gastrointestinal disease, especially diverticulosis. You may help minimize attacks and improve treatment results by following specific dietary recommendations.
- While few studies have examined the effectiveness of specific homeopathic remedies, professional homeopaths may recommend one or more of the following treatments for diverticular disease based on their knowledge and clinical experience. Before prescribing a remedy, homeopaths take into account a person's constitutional type, includes your physical, emotional, and intellectual makeup. An experienced homeopath assesses all of these factors when determining the most appropriate remedy for a person.
- Belladonna is used for abdominal pain and cramping that comes on suddenly and feels better with firm pressure. It is particularly helpful if constipation accompanies the pain.
- Bryonia is used for abdominal pain that worsens with movement and is relieved by heat. It is particularly useful if vomiting or constipation with dry, hard stools accompanies the pain.
- Colocynthis is used for sharp, cramping abdominal pains that improve with pressure. It is particularly useful if the pain is accompanied by restlessness and diarrhea.
- Acupuncture may help relieve pain and other symptoms. Acupuncturists treat people with diverticular disease based on an individualized assessment of the excesses and deficiencies of qi (or energy) located in various meridians. Acupuncture and Chinese medicine in general may promote gastrointestinal health.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...