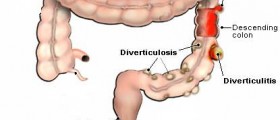
Acute Diverticulitis
Acute diverticulitis is inflammation of diverticula, specific pouches which commonly affects large intestines. Diverticulosis and consequent diverticulitis develops as a result of increased pressure inside the intestines and weakness of the layers of the intestine wall.
Causes of Acute Diverticulitis
The exact cause of acute diverticulitis has not been established yet. However, many believe that lack of fiber in everyday diet may be one of the reasons why diverticulosis and consequent diverticulitis occurs. Insufficient intake of fibers causes constipation and increased pressure in intestines. The pressure may be so intensive and cause pouching of the weak parts of the intestinal wall. Pouches or sacs are excellent place for accumulation of feces and bacteria and this is what seems to cause inflammation.
Another cause of diverticulosis and diverticulitis can be thickening of the colon wall which is predominantly age-related problem.
Symptoms of Acute Diverticulitis
Most patients suffering from diverticulitis have no symptoms at all. In this case the disease is classified as asymptomatic. Still, in case of inflammation of diverticula symptoms become obvious and start to bother patients.
The leading symptom of acute diverticulitis is abdominal pain. It may or may not be accompanied by stomach cramps. Nausea and vomiting occur as well. Irregular bowl movements such as diarrhea and constipation are also typical for acute diverticulitis. And finally, some patient may develop fever.
In rather rare cases diverticulitis can be followed by rectal bleeding or the presence of the blood in stool. Luckily this complication is not so common.
Treatment for Acute Diverticulitis
This medical condition requires proper treatment after definitive diagnosis has been set since if left untreated it may cause bleeding and potential rupture or even obstruction in the colon.
One of the complications of acute diverticulitis is abscess. Inflamed and infected intestinal wall may also perforate leading to peritonitis. This complication requires prompt surgical repair. Furthermore, there is even chance of fistula formation. Connection can be established between intestines and other organs in abdominal cavity such as bladder. Fistulas also require surgical repair.
To prevent all of the previously mentioned complications patients are prescribed oral antibiotics and surgery may be performed if there is a risk of certain complications or in case that complications have already occurred. Furthermore, patients are required to change their dietary regimes. They need to stick to juices (without pulp), clear soup, and plenty of plain water. Liquid diet is essential in healing of the inflammation and it also prevents some of the potential complications. Those who have suffered acute diverticulitis need to change their diets and start consuming foods rich in fibers to prevent recurrent inflammation.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...