Diverticulitis is a disease associated with bursting of diverticula in the colon, which may lead to an infection of surrounding tissues.
Diverticulitis Overview
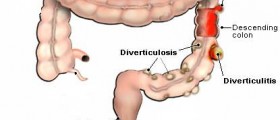
The large intestine (the colon) is the part of the digestive system which stores and eliminates waste material. Due to elevated pressure within the colon, small, bulging pouches may form in the wall of the colon. These pouches or bulging pockets of tissue that push outward from the wall of the colon are known as diverticula.
Diverticula may form anywhere in the colon but it is most commonly seen near the end of the sigmoid colon. Development of diverticula in the colon is known as diverticulosis or diverticular disease. This condition may produce few or no symptoms.
However, if diverticula ruptures it is known as diverticulitis and is accompanied with fever, abdominal tenderness and pain in the abdomen. Diverticulitis can also cause diverticular bleeding. Causes of Diverticulitis
Among population of the Western world, diverticulitis is a common disease. On the other hand, the condition is very rarely seen in Asian and African population. Age is also a significant risk factor for diverticulitis. In the United States, the condition does not affect individuals under age of 40 but is very common in people over the age of 60.
With increasing age, the colon tends to weaken and its wall to thicken. Increased pressure in the colon, often caused by constipation causes development of abnormal pouches on the outside of the organ resulting in diverticulitis.
This can be seen in individuals who eat diet low in fiber. They usually have difficulty passing stool, which elevates the pressure inside certain portions of the colon and leads to formation of pouches in the colonic wall. Pieces of stool may get trapped in diverticula resulting in infection and inflammation.
Symptoms of Diverticulitis
Diverticulosis can be asymptomatic and discovered incidentally during medical tests done for other reason. Some individuals with diverticulosis develop symptoms such abdominal cramping, bloating, constipation and diarrhea.
Complications may occur if one of diverticula ruptures causing the bacteria to spread to the nearby tissues within the abdomen. Abscess in the pelvis may develop when pocket filled with pus forms around inflamed diverticulum.
Sometimes an inflamed diverticulum may adhere to the urinary bladder and cause bladder infection and passing of intestinal gas in the urine. Colonic bowel obstruction can also result out of diverticulitis. Rarely, rupture of a diverticulum can cause waste matter to leak into the abdominal cavity leading to a life-threatening infection known as peritonitis.
Rectal bleeding may occur as well and can be continuous or intermittent. Patients with continuous bleeding need to be hospitalized and treated as in severe cases this bleeding can cause drop in blood pressure, dizziness, shock and loss of consciousness. Severe bleeding can be stopped by surgical removal of the bleeding diverticulum.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...