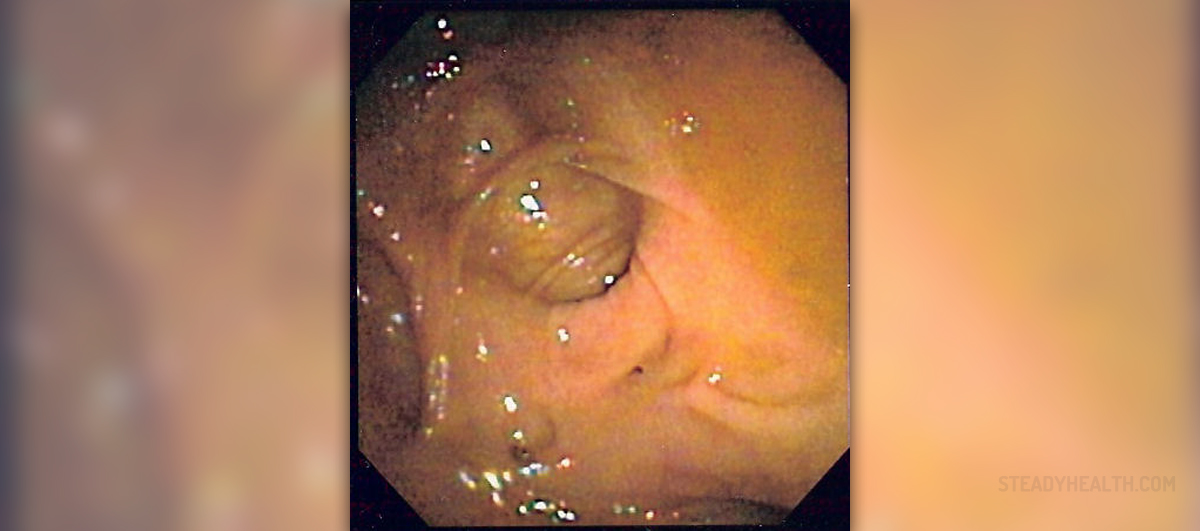
Diverticulosis is a medical condition that features with pockets (pouches) in the large intestine. The large intestine is a long tube-like structure that stores and eliminates waste material. Due to the process of aging permanent pressure inside the large intestine may cause formation of bulging pockets of tissue or sacs (diverticulum) that push out from the colon wall.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diverticulosis
The condition rarely affects people younger than 40. It is estimated that around 30% of people older than 45 develop diverticulosis. The older the person the greater chances for him/her to develop the condition. Apart from obvious connection between the age of a person and the occurrence of diverticulosis the chances of the condition development are also associated with genetic predisposition and with diet low in fiber.
Symptoms of Diverticulosis
Majority of patients have few symptoms. The condition can also be completely asymptomatic. Symptomatic form of the disease is classified into three types: painful diverticulosis, inflammatory diverticulitis (the type that develops due to inflammation and infection of diverticula) and bleeding diverticulosis.
Patients suffering from painful diverticulosis complain about abdominal pain (located in the lower left abdomen), constipation followed by bouts of diarrhea and bloating. The pain may subside after a bowel movement. Inflammatory diverticulitis features with abdominal pain, constipation, fever, bloating and vomiting. And finally, bleeding diverticulosis typically features with sudden and mild cramps, urge to defecate, bright red blood clots and maroon-colored stool. Excessive loss of blood may cause anemia and fainting.
Treatment for Diverticulosis
In case a person does not have any symptoms at all he/she does not require treatment. However, even these patients are advised to make dietary changes and consume a lot of food rich in fiber such as vegetables, fresh fruits, whole-grain breads, cereals and bran. The diet may also include fiber supplements while small seeds (strawberries, raspberries, whole cranberries and nuts) should be avoided. Patients who suffer from bloating and abdominal pain may be prescribed antispasmodic drugs. Diverticulitis requires bed rest, antibiotics and in some cases hospitalization. Surgical procedures are reserved only for patients who have developed an abscess caused by a ruptured diverticulum. Surgery is also performed in patients with severe or multiple attacks.
Prevention of Diverticulosis
In order to prevent diverticulosis one must maintain good bowel habits. This particularly refers to regular bowel movement. People must prevent constipation and if it occurs treat it properly. Straining is not recommended either. Intake of food rich in fiber is good preventive method against diverticulosis. And finally, one should drink plenty of water and engage in regular physical activity.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...