What is there to resist?
Resistance training is such form of the exercise in which muscle force opposes an external force (weight, friction, etc). There are basically two phases of resistance training. In the first phase, muscles become adapted to the initial opposing force. In the second phase, opposing force is increased in order to initiate further adaptation to the new, more powerful stimuli. Once the muscles are adapted to the increased level of opposing force, making it 'default', the force is further increased, and so on.
Goal of resistance training is increase of strength and size of skeletal muscles. Results obtained by resistance training depend on factors such as adequate selection of training program, variations in training program and individual adaptations of the program to the person.
Health benefits
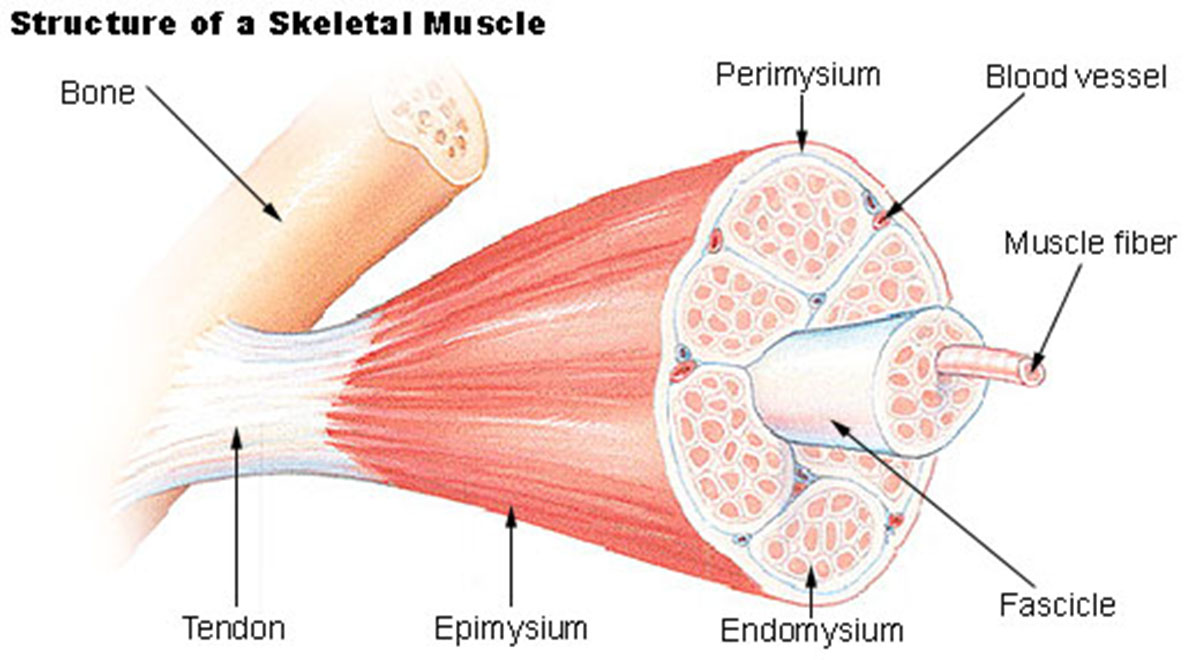
Resistance training programs induce physiological changes that are related to various health benefits. Primary and most visible effect is on muscle cells. These cells are usually referred to as muscle fibers due to their extremely elongated shape that resembles human hair. Muscle fibers adapt to resistance training through increase in size, a process referred to as hypertrophy. Lasting hypertrophy is obtained and maintained through constant exercise and ranges from 20 percent to 45 percent increase in individual fibers' circumference.
Hypertrophy is result of changes within the muscle cell such as increase in number and size of cell's internal structures, and increase of the connective tissue around the muscle fibers, which all lead to increased power of the muscle. However, number of muscle cells in a human organism is constant, determined at birth, and does not increase.
Neural pathways used for muscle control also develop in the course of exercising, in order to enable better muscle control and extract more force from a single fibre, thus creating a more 'exercised', stronger and quicker-responding muscle.
It should be noted that there are muscles responsible for fast movements and muscles responsible for slow movements, which are trained by fast speed exercises and slow speed exercises. Each type of exercises is beneficial to the specific type of muscles it is targeted at.
Another great, although less visible impact of resistance training is adaptation of bones to increased levels of force generated by muscles. Bones of every organism are constantly remodeling, and increase in stress and load on the bone leads to construction of a more powerful bone, able to sustain such forces. There are various exercise programs that aim to improve of bone quality.
Other significant, long term adaptations to resistance training include physiological changes such as increase of heart size, which enables the heart to pump more blood with more force, reductions of blood pressure and heart rate at rest, both highly beneficial to the circulatory system, and metabolic adaptations that lead to increased energetic efficiency. Resistance training also affects lipoprotein and lipid levels in the body, reducing risk of coronary heart diseases and reducing body fat levels.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...