Introduction
The humeral shaft is the area that extends from the upper part of the pectoralis major tendon all the way to the supracondylar ridge.
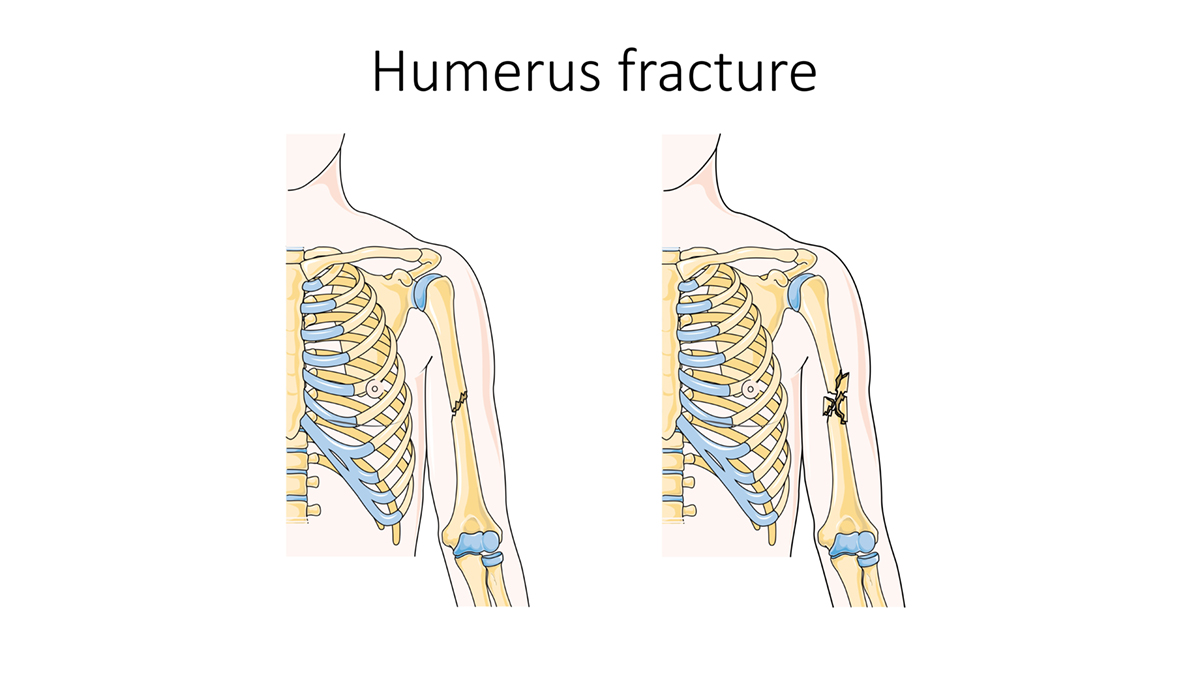
A humerus fracture is an injury that occurs in the bone that is located in the upper arm. The humerus connects the shoulder to the elbow, essentially.
There are three different types of fractures—proximal, mid-shaft, and distal.
Proximal fractures occur near the shoulder joint and could involve an insertion of the rotator cuff tendons. Since these tendons are essential to the motion and movement of the shoulder, the treatment options will often depend on the position of these tendons.
Mid-shaft fractures occur away from the shoulder and elbow joints will most likely require surgery. They are also commonly associated with injuries to nerves in the arm, the radial nerves to be precise. Symptoms in the wrists and hands may occur as a result of these nerves being injured. Distal fractures are not common in adults and usually happen in children. They are fractures that occur closer to the elbow joint, and the treatment of this fracture will depend on whether the patient is an adult or a child.
Treatments
Most humerus fractures will heal without the use of any surgical operations. Usually a patient will have to wear either a sling or a brace and in time, the fracture should heal on is own.
Surgery
Almost every fracture of the humeral shaft is unstable, but can usually be treated without an operation.
Whether or not a patient should have the surgery depends on the characteristics of the fracture.
Patients who have these types of fractures usually experience pain, deformities and swelling in the arms. The arm is usually shortened and the motion of the arm is compromised. This limb must be documented and looked at very closely, and surgery should be considered as an option for a number of reasons.
A good reason to opt for the surgery is the fact that the closed methods of treatment might not be able to align the fracture well enough.
Surgery is often required when the bone fragments that are fractured are too far out of position. Usually the injuries that require surgery are located closer to the joints, and the ones that can heal on their own are located in the middle of the bone shaft. When the injury occurs further away from the joints, the bone fragments are able to be aligned much easier and more effectively.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...