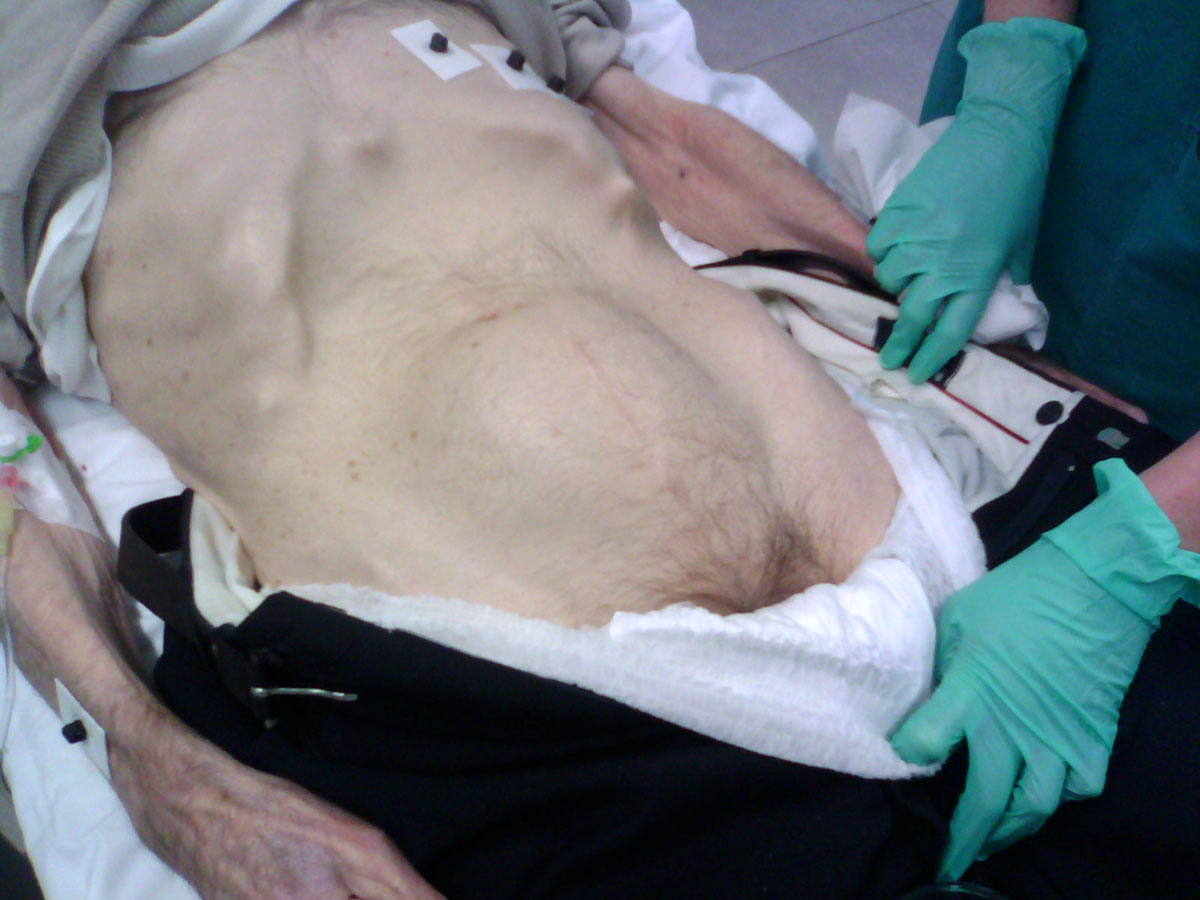
Urinary retention can be defined as a condition that features with incomplete emptying of the bladder. It can affect both genders and develop due to a variety of causes and factors. In urinary retention the urine is withheld in the bladder and cannot be adequately eliminated. Urinary retention can be classified as acute or chronic. In acute form of the disease retention develops suddenly while in chronic urinary retention there is always some urine left in the bladder and the organ is never completely emptied.
What Causes Acute Urinary Retention in Men?
Urinary retention is more common in elderly men. There are many diseases and conditions associated with urinary retention in men.
In many cases acute urinary retention develops as a consequence of obstruction. The blockage in urine flow can develop due to benign prostatic hyperplasia, bladder stones or cancers. Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects older men, it is a benign condition in which the prostate enlarges and blocks the urine flow through the urethra. Bladder stones may become large and interfere with elimination of urine. And finally, cancer of the bladder or the prostate may be responsible for the obstruction once it has grown to a certain size (or due to its localization).
Urinary retention may also be connected to the the presence of foreign bodies in the urinary system, strictures (narrowing of the urethra or other parts of the urinary tract usually connected with scarring) and bladder diverticula. The retention sometimes affects people who drink too much, may occur due to urinary tract infections and intake of certain medications. And finally, urinary retention affects men who have suffered damage to the nerve that innervate the bladder.
Clinical Characteristics of Acute Urinary Retention in Men
In many cases retention leads to slow urinary flow. One may not be able to urinate at all. The bladder can enlarge and cause pain or stiffness in the lower abdomen, lower back, hips or upper thighs. If the retention is only partial one may feel like he has not completely emptied the bladder.
Treatment for Acute Urinary Retention in Men
The goal of the treatment is to restore a normal flow of the urine and eliminate all the symptoms and signs of the condition. Many men need to be inserted a catheter that remains only temporarily or stays for a longer period of time. The treatment actually depends on the underlying condition that has led to urinary retention in the first place. In general, treatment is either conservative or surgical. Conservative approaches include different medications such as antibiotics, alpha blockers and hormones.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...