Pulmonary Tuberculosis and the Main Facts
Pulmonary tuberculosis is a very serious and contagious disease that is caused by the bacteria. The seriousness of this condition is implied through the fact that it is one of the major causes of death all over the world, even though it can be successfully treated and cured when discovered in time. When setting the diagnosis, it is very important to determine whether it is active or latent though it can easily be concluded based on the symptoms as well.
The main symptoms of active tuberculosis, which is contagious, are night sweats, loss of appetite and weight without a logical explanation, fatigue, and fever, while in cases of latent, none of the symptoms have to appear.
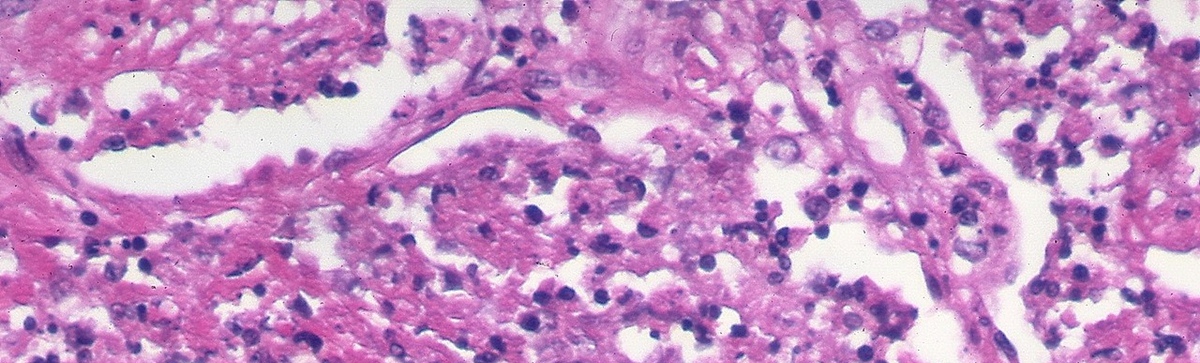
The signs that indicate pulmonary tuberculosis are pain in the chest, coughing which lasts for several months, and coughing up blood. Besides the treatment that consists of medicines, this serious condition can also be treated with some homemade and herbal remedies, and if they are given a chance, they will prove to be very helpful.
Complications of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Having in mind that pulmonary tuberculosis primarily affects the lungs, lung damage is one of the most frequent complications, and it may lead to lung failure. However, when it comes to the other possible complications that tuberculosis can cause, the greatest majority of them are very serious, and even life-threatening, especially in cases in which this disease is left untreated or in cases in which it has not been treated timely and properly. In such cases, it may spread to other parts of the body, thus making the treatment more difficult, particularly if it spreads to the bones because the destruction of the joints followed by pain is very likely to be experienced then.
- A prospective observational study was conducted, the study included all patients presenting with complications of tuberculosis in newly diagnosed and previously treated patients referred to the Pulmonary Medicine Department. Patients not willing to give consent for the study or the patient with incomplete data were excluded. TB was diagnosed on the basis of sputum Gene Expert, Line Probe Assay and Conventional Drug Sensitivity testing.
- Of the total 310 cases, 176(57%) patients were males and 134(43%) were female patients. The mean age of all patients was 41.72 years. Among the 310 cases 293(95%) were drug sensitive tuberculosis and 17(5%) patients were of drug resistant tuberculosis. Out of the 310 patients; 160(51%) patients had post TB COPD as complication of TB. Most common complication was post TB COPD while least common was BPF seen in 8(2.5%) patients.
- The most common co-morbidity was DM which was seen in 15 (5%) patients. Cough was most common among various symptom with which patient presented to hospital. Out of 310 patient who had complication due to tuberculosis 301(97%) patient were hospitalised and 9(3%) patients were treated on OPD basis. Most common complication which leads to hospitalisation was post TB COPD with or without respiratory failure.
Meningitis is practically an inevitable complication in cases when pulmonary tuberculosis spreads to the brain, and it is important to mention that this condition may be fatal. The seriousness of this disease is implied through the fact that it can spread to the entire body, and in such cases, it leads to the failure of the kidneys, liver, and even heart, which is the reason for many fatal outcomes related to this complication.
Infants, older people, and those with lower immunity are particularly at risk of developing complications, which is why it is extremely important to react as soon as the first symptoms are noticed.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...