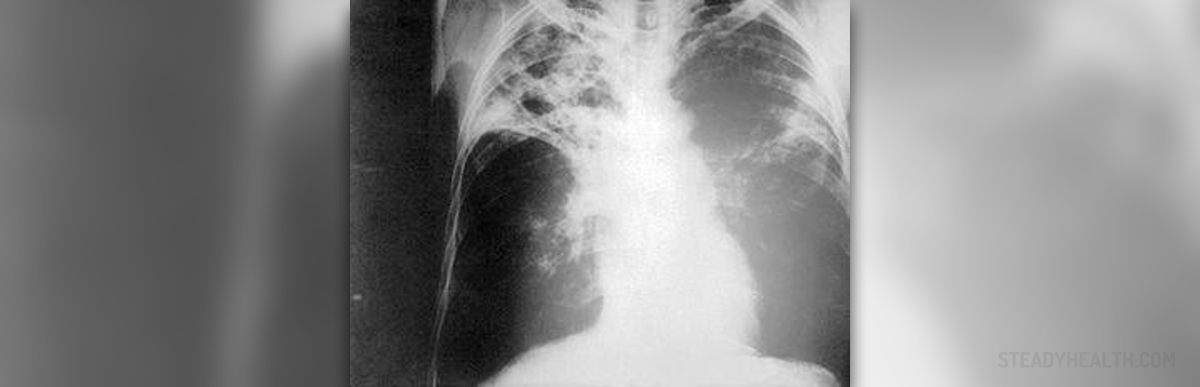
About 2 billion people in the world are infected with tuberculosis bacterium but the disease develops in 1 of every 10 people. Africa and South East Asia are known as the countries with most diagnosed cases of tuberculosis (TB). Developed parts of the world are much less likely to be associated with TB, but this disease can still be found in some of the biggest cities of the world.
Lung infection
Tuberculosis is usually an infection of the lungs, provoked by bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB may also affect the skin or some other organs as well. A person suffering from TB may transfer the disease through tiny sneeze or cough droplets. Healthy immune system is usually able to deal with this infection but if that’s not the case (due to some weakened immune system, poor control of the diabetes, underweight or HIV infection) the person gets TB. In some cases, immune system forms defensive barrier around the infection. These patients don’t have any symptoms and can’t pass the infection to anyone else (latent TB).
Symptoms of Tuberculosis
TB symptoms may not be present in a certain number of patients. Other will have minor problems or some signs showing in several months or even years after infection. Patients usually experience: persistent cough with phlegm or blood sometimes, fever, poor appetite, weight loss and tiredness. Some people suffering from tuberculosis may notice night sweating or chest pains when inhaling the air.
As mentioned before, TB usually affects the lungs (pulmonary TB), but it spreads through the lymph nodes and may end up infecting the joints, bones or even kidneys and in some rare cases the membranes around the brain and spinal cord (meningitis). TB is therefore also associated with pain in the joints, swelling of the lymph nodes or headaches, depending on the part of the body affected with the disease.Risk Groups
Some people may be exposed to a greater risk of catching tuberculosis than others. This is found out to be especially true for people with weakened immune system, diabetics, young or elderly patients, drug and alcohol addicts and people with poor health. Also, everyone in close contact with people with TB lung infection and those living in overcrowded housing may also develop this condition much easier than anyone else.
Tuberculosis Prevention
In order to prevent TB, The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies and treats people suffering from tuberculosis and all of their contacts. Vaccination of children is also on WHO agenda, but there are vaccines for adult people. However, doctors found out that exposure to non-tuberculous Mycobacterium may be helpful protection from TB in adults.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...