Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious and potentially disabling infectious disease that affects people all over the world, particularly people in developing countries. The infection is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and may also develop due to Mycobacterium bovis (which rarely occurs nowadays).
Tuberculosis Overview
Tuberculosis predominantly affects the lungs and mediastinal lymph nodes. However, in some patients, particularly those who are not treated on time as well as immunocompromised patients, the bacterium may spread to other organs and tissues such as the kidneys, bones and the brain.
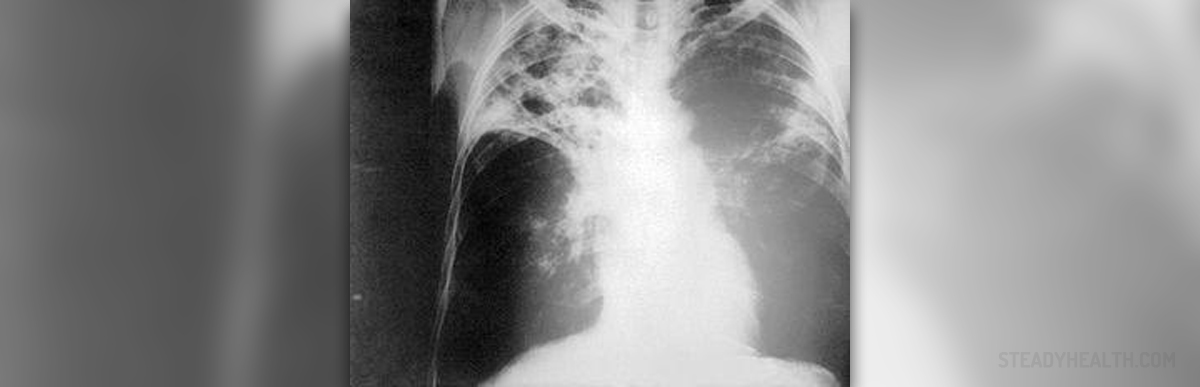
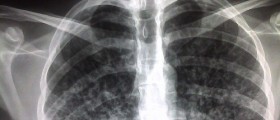
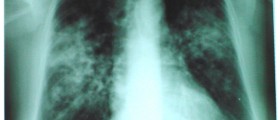
Pulmonary tuberculosis initially leads to fever, dry cough and structural abnormalities which can be easily identified on chest X-ray. Primary pulmonary tuberculosis may withdraw spontaneously or it may eventually return. Once the infection returns, it causes severe damage to the lung tissue, especially the upper parts of the lungs. Patients cough and there is increased production of mucus. They may even cough up blood. Additional symptoms and signs of recurrent tuberculosis include fever, loss of appetite accompanied by weight loss and night sweats.Prevention of Tuberculosis
It is essential to mention that the only contagious form of the disease is active tuberculosis. In some individuals tuberculosis can be found by testing. They may have latent infection and need to be treated so that the infection does not progress into an active form. This way such patients are properly protected against active form of the disease and all its detrimental effects.
Furthermore, in case an individual is suffering from active tuberculosis it is important to protect all the individuals who are in close contact with the infected person, particularly family members and close friends. Such individuals are supposed to stay at home and avoid close contact with healthy people during the first few weeks of treatment. The room a person is staying in should be frequently ventilated. The patient is due to cover his/her mouth each time he/ she laughs, sneezes or coughs. The tissue should be thrown away immediately after these activities. And finally, one more way of adequate protection includes wearing a mask which can successfully prevent transmission of the infection during the first three weeks of the treatment.
All patients must finish the entire course of antibiotics even though this may last for several months. Only this way bacteria can be completely eradicated. Otherwise microorganisms may mutate and develop resistance which makes further treatment more difficult.
And finally, in countries in which this infections is considered frequent, all infants are routinely vaccinated with bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine. By doing so children are properly protected against severe forms of tuberculosis during their childhood.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...