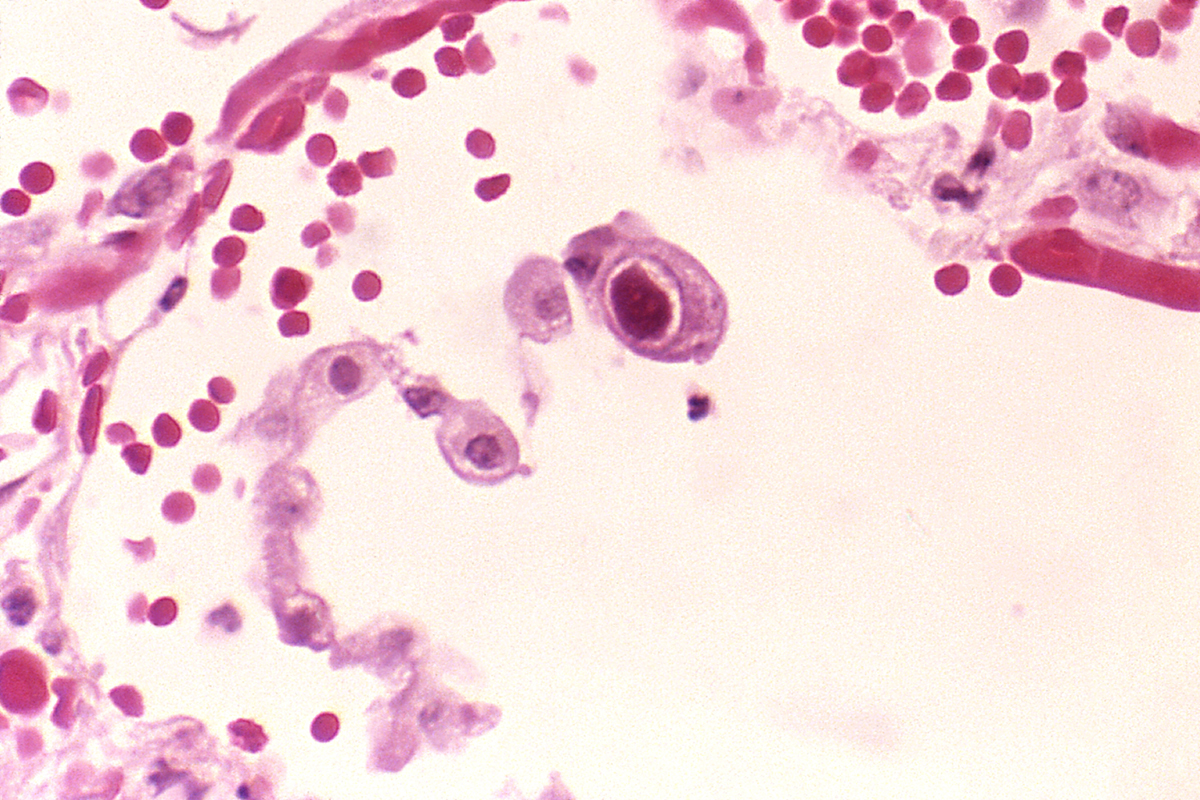
Introduction to fungal lung infections
A fungus can in some cases cause long problems, especially through infections of the pulmonary tissue or by triggering immunological reactions when fungus is inhaled.
Usually such infection are not present in a significant degree, expect maybe aspergillus-induced asthma, in western countries. These problems may affect people traveling to more exotic places where there is more of a change of contracting such infections, especially people who have poor immune systems due to recent organ transplants or serious health problems such as cancer or HIV.
Pulmonary infections can occur after a person has inhaled spores or through a reactivation of latent infections.
One of the most common fungal lung infections is aspergillosis, which can often spread to there organs as well and be very dangerous.
Some of the conditions most common symptoms include chills, fever, shock, delirium and blood clots. Kidney failure is a common complication as is liver failure and serious breathing problems.
The condition can eleven be fatal if not treated on time.
When the fungal infection spreads to other organs, the complications can be very serious. It can even cause itching in the ear canal and sometimes a person may see stains on the pillow from fluid draining from the war. The lung infection can also cause sinus problems and congestion as well as painful discharges in some instances.
Diagnosis
Doctors will usually diagnose a fungal lung infection based on the symptoms that appear in the individual.
Sometimes, an x-ray will be used to pinpoint the infected area and make a diagnosis.
Doctors will like to have infected materials to sample and cultures from the lung in order to be able to identify the fungus that is causing the problems as well.
Treatment
When the infection is in the lungs it does not pos an immediate problem and the onset of the symptoms is fairly slow, but it does need to be treated right away, since the condition does get more serious as the infection spreads.
Most of the infections are treated with antifungal drugs such as amphotericin B. However, there are some forms of infections that do not responded to these drugs and might have to be treated with caspofungin, which is a more intensive anti-fungal.
When the infection spreads to the ear canal, the doctor may treat it by scraping the fungus out or apply ear drops of antifungal drugs.
Fungi deposits in the sinuses sometimes must be removed surgically. If the fungus balls in the lungs grow near the blood vessels, then they might have to be removed surgically as well because they can invade the vessels and lead to heavy bleeding.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...