Tuberculosis is a perfidious disease that may lead to serious damage of the lungs and is also able to spread to distant tissues and cause additional damage to many organs and organ systems such as bones, kidneys, central nervous system, joints, etc.
The infection is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The infective agents are inhaled. Once the person gets infected, there are several possible outcomes. The infection can be in the form of an active disease.
Furthermore, in the latent form of tuberculosis, the infective agent stays in the body and is not active for a certain period, but it can become active under certain circumstances. In case infective agents spread to distant organs in the body, the disease is classified as generalized tuberculosis.
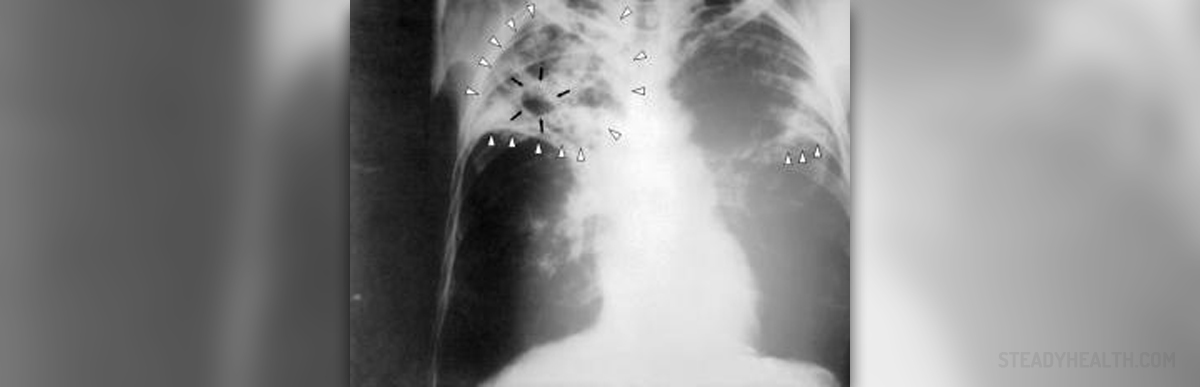
People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to tuberculosis, and they commonly develop a more serious form of the disease. Tuberculosis can be classified into contagious and non-contagious tuberculosis.
Contagious Forms of Tuberculosis
One type of contagious tuberculosis is primary tuberculosis pneumonia. This is a very contagious form of the disease that features similar symptoms and signs as classic pneumonia. Primary tuberculosis pneumonia most commonly affects immunocompromised patients. Laryngeal tuberculosis is another contagious form of the disease. This form of tuberculosis affects the larynx.
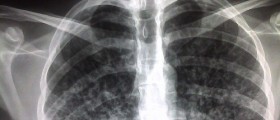
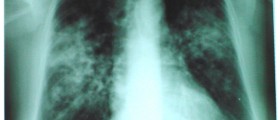
There are a few more contagious forms of tuberculosis. They include miliary tuberculosis, tuberculosis pleurisy, and cavitary tuberculosis. Miliary tuberculosis is a serious form of disease that develops soon after the infection is contracted. In miliary tuberculosis, the infection affects many parts of the lungs. In tuberculosis pleurisy, the infection predominantly affects the pleura.
And finally, cavitary tuberculosis features severe damage to the lung tissue. The damage is in the form of cavities and leads to chronic cough. By coughing, one may spread the infection to other people.
- Smear-negative patients can and do transmit TB. Such patients accounted for 17% of secondary transmission in San Francisco. There is also evidence that some mycobacteria are much more infectious than others.
- Community studies suggested that within stable households, transmission to identified contacts (with long-standing antecedent exposure) greatly diminished or ceased once effective treatment was initiated. However, most of these studies had serious design flaws. The only randomized controlled trial of confinement versus outpatient treatment took place in India, where nearly all contacts evaluated were already infected.
- Multidrug resistance is uncommon in Canada (1-2% of cases), but resistance to isoniazid was seen in 8.7% of Montreal cases. In these patients, the response to standard therapy may be slower (or nonexistent, in multidrug resistance cases). The laboratory diagnosis of drug resistance cannot be established within 2 weeks.
Non-contagious Forms of Tuberculosis
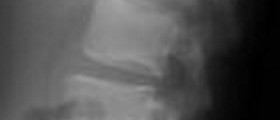
Osteal tuberculosis is an infection of the bones. Mycobacterium tuberculosis spreads from the lungs to the bones and causes damage. Damage to bone tissue may eventually lead to bone fractures.
Tuberculosis meningitis is another non-contagious form of the disease. In this form of tuberculosis, the meninges are damaged by a direct influence of bacteria.
There are several more non-contagious forms of tuberculosis. They include renal tuberculosis, adrenal tuberculosis, etc. Even in case the bacteria have spread to lymph nodes, there is no chance of further transmission of the disease.
Non-contagious forms of tuberculosis represent the advanced stage of the disease which occur once the bacteria spread from the initial place of the infection, the lungs. These forms are much harder to be treated and lead to serious complications. The best effects of the treatment are achieved if the condition is diagnosed on time and in case the damage to the lung tissue is limited.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...