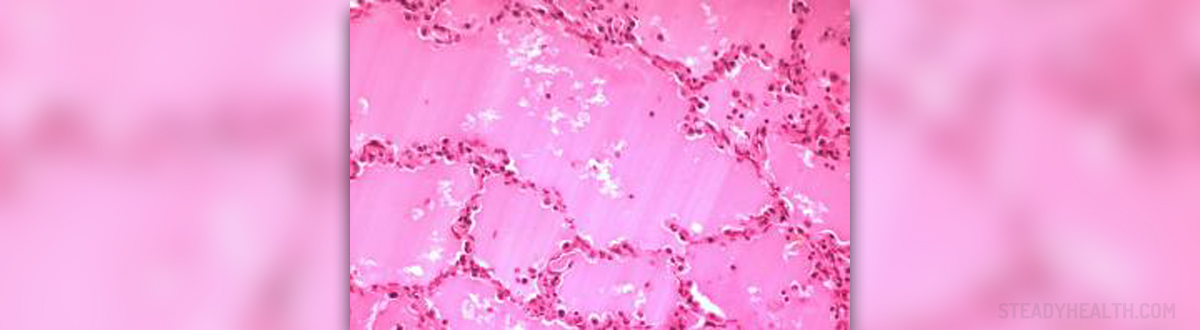
Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema is swelling of the lung tissue caused by excessive accumulation of the fluid. The fluid comes out from the blood vessels and accumulates in the surrounding tissue. This can be result of either increased blood pressure in blood vessels or can develop due to insufficiency of the proteins in the bloodstream.
In pulmonary edema the fluid collects in alveoli. Alveoli are the terminal part of the lung tissue that are in charge with exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. In case of the presence of fluid the thickness of alveoli increases and appropriate exchange of gasses cannot be achieved. This consequently results in difficulties with breathing such as shortness of breath and feeling of choking. This life-threatening condition may be a result of certain heart conditions, particularly heart failure or it can related to other diseases. This is why all the pulmonary edema is classified into cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is related to certain heart conditions. Insufficient function of the heart muscle leads to high blood pressure in lung blood vessels. The heart muscle cannot pump the blood properly because of arrhythmia or some other functional or structural problems. Pulmonary edema is typical in heart attack. This complication of heart attack can lead to death if not treated properly and on time.
Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema can be caused by some other medical conditions apart from heart diseases.
For example, it can occur in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Acute respiratory distress syndrome can be a consequence of infections, trauma or injury of the lung tissue, inhalation of toxic substances or radiotherapy of malignant tumors of the lungs. In this case inflammation of the lung tissue is what leads to fluid collection within alveoli.
People who are suffering from kidney failure can also develop pulmonary edema. Namely, the kidneys cannot function properly and they cannot eliminate the fluid from the body. Consequently, the excess of fluid within the body leads to pulmonary edema.
Pulmonary edema can also develop due to high altitude and inappropriate adaptation to its effects.
Intracranial bleeding or brain trauma as well as severe seizures can in certain cases lead to pulmonary edema.
Rapid expansion of the lungs can consequently result in pulmonary edema. This situation develops after treatment of pneumothorax or pleural effusion. In people who are suffering from these conditions secondary pulmonary edema almost always affects only one lung.
Heroin or methadone overdose can be another cause of pulmonary edema. Even overdose with some prescribed medications, such as Aspirin may lead to this severe condition.
And finally, pulmonary edema can result from pulmonary embolism, develop after viral infections or be one of the complications of eclamsia which is a medical condition that affects pregnant women.














_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...