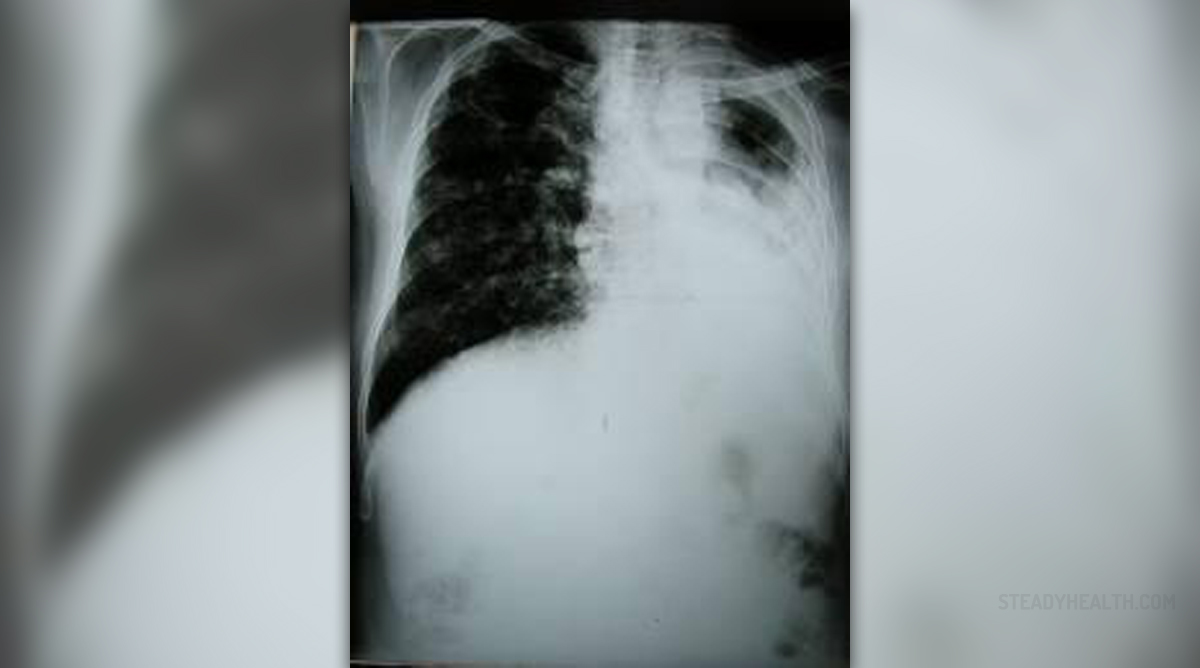
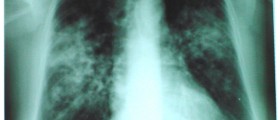
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that affects patient’s lungs. This infection may be very serious, and in some cases even fatal. This severe infectious disease is caused by different strains of mycobacteria. In humans, the Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the most common cause of the disease. Lungs are mostly affected, but the disease may even spread to the rest of the body. If left untreated, tuberculosis will most probably kill the patient. The mortality rate in these cases is estimated to more than 50 percent.
Signs and symptoms of tuberculosis
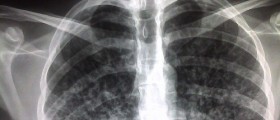
In most of the cases, humans infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis will do not have any symptoms. It is estimated that about one third of population currently has Mycobacterium tuberculosis in their bodies. In one in ten patients, tuberculosis will progress from the latent infection to active disease, which has to be treated. In the active stage, lungs are going to be affected, and the patient will start showing symptoms of chest pain, coughing up blood, fever, chills, night sweats, weight and appetite loss, pallor and extreme fatigue. Patients suffering from tuberculosis usually have a specific odor, and some trained animals may even help in early detection of the problem.
Causes and risk factors
Tuberculosis is usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which can withstand weak disinfectants and survive in a dry state for weeks. This bacterium divides at a very slow rate, every 16 to 20 hours. Mycobacterium tuberculosis includes various subtypes such as M. bovis, M. africanum, M. canetti and M. microti. M. africanum, M. canetti usually affects people in Africa. M. bovis is not as severe as it used to be, since the introduction of pasteurized milk. M. microti normally affects people with the compromised immune system. Other risk factors that may contribute to disease are underlying silicosis (a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust), low body weight, diabetes, and using certain drugs that work by blocking tumor necrosis factor-alpha (such as medications for rheumatoid arthritis).Prevention of tuberculosis
When a person is positive for latent tuberculosis infection, there is a lot one can do to reduce the risk of developing active tuberculosis and spreading the disease to other healthy people. Tuberculosis is contagious only when it affects the lungs, in the active stage. Patients should stay at home and avoid sharing the room with other people, in the first couple of weeks of treatment. The room should be ventilated often, and the patient should cover the mouth when laughing, sneezing or coughing. It is also recommended to wear a surgical mask and to put dirty tissues in a sealed bag before throwing them away.
Vaccine is also available but it is used only in the countries with high rate of infection. It is mostly efficient on children, but not on adults.









-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...