What is candidiasis?
Candidiasis means an infection with fungus species belonging to the genus Candida, most commonly Candida albicans. Candida fungi are the most common fungi that affect humans and they are present virtually everywhere. They are present in the human body as well, but they do not necessarily cause an infection. Due to certain factors, an overgrowth of fungi occurs, leading to infection and its symptoms.
Candida causes several different mucosal and systemic diseases, ranging from mild and superficial mucocutaneous infections to invasive diseases affecting internal organs, such as hepatosplenic candidiasis, Candida peritonitis and systemic candidiasis.
These yeast-like fungi can be found almost anywhere, from human and animal skin, hair, organs and mucous membrane to foods, floors, countertops, vents and such. Contracting Candida does not necessarily mean getting infected or developing a serious, invasive or systemic disease. Candidiasis or yeast infection can be mild and easily treatable, especially on the skin. However, certain factors may increase the risk of developing more serious forms of this disease, and those include weak immune system, severe trauma, recent infections, the use of corticosteroids, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, premature birth, burns, hematologic problems and many more.
Chronic candidiasis
As mentioned above, Candida can cause an infection that is easily treated with anti-fungal medication, whether it is oral or topical. However, sometimes an infection with Candida is particularly persistent, with a protracted course. This can be seen in mucocutaneous candidiasis, a form of Candida infection that can affect the skin, the nails, hair and mucous membrane.
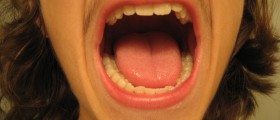
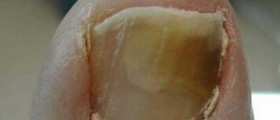
Chronic candidiasis usually starts in the childhood or in the first 20 years of life. It rarely starts after the age of 30. The symptoms of candidiasis that are constantly present include lesions on the skin or the face, scalp, hands and nails. Oral thrush is also commonly associated with it.
This disease can and must be treated, or the treatment should at least be attempted. The problem with chronic candidiasis is that it obviously does not respond to the usual anti-fungal treatment but such treatment is, in most cases, able to at least slow inhibit the progression and spreading of the infection and to alleviate the symptoms to a certain extent.
Chronic candidiasis is not very common. It seems to be associated with diseases and conditions affecting the endocrine system, such as hypoparathyroidism, Addision disease, diabetes mellitus, thymomas, polyglandular autoimmune disease and such.
The treatment for this disease depends on many factors, but it generally consists of systemic anti-fungal therapy and certain immunologic therapies.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...