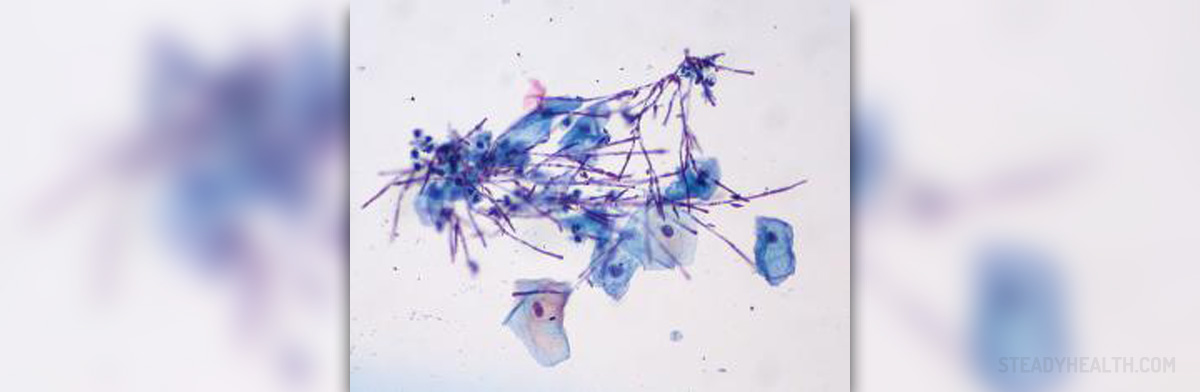
Candida - Female Genital Tract Nightmare
Fungal infections of the genitals are mainly caused by the fungus Candida albicans and are very common in women. Candida albicans is normally found in the intestines and the skin. An excessive fungus multiplying occurs when immunological balance is disturbed for some reason or because of some external influence.Causes
Environment rich in carbohydrates is suitable environment for the development of Candida and therefore the most often causes of candidiasis are: pregnancy (pregnancy vagina is rich in glycogen) unregulated diabetes mellitus - blood and body fluids have more sugar in patients with poorly regulated diabetes, which makes them a better base for the development of microorganisms, including fungi - Candida albicans, which then causes the infection applying a wide range of antibiotics which suppress the normal flora immunosuppressive therapy using contraceptive pills excessive hygiene of the genitals using alkaline soaps, which destroy the normal flora of mucous membranes menstruation synthetic underwear and tight clothing inadequate sanitary padsvaginal washings perfumed hygiene sprays local antimicrobial therapySymptoms
The most common symptom is intense itching and irritation in the vagina and vulva. Secretion is a whitish, thick as cheese and odorless. Redness is a sign of inflammation and the vagina is covered with cheesy white colonies of fungi. Vaginal pH is <4.5. About 20% of women are without symptoms.The symptoms are especially pronounced after sexual intercourse because friction further enhances sense of burning and itching. Also pain may occur in women after sexual intercourse. Itching can be spread to the area around the anus.
Since the gastrointestinal tract is reservoir of Candida, candidiasis recurrences and reinfections are frequent. The cause of reinfection can be sex with an infected partner, although it is rare.
If a diagnosis of recurrence is confirmed, the oral glucose-tolerance test should be done to determine forms of carbohydrate metabolism disorder. A systemic treatment to eliminate infection in the intestines should be applied in the case of recurrent infection.
Connection of menstruation with the infection recurrence (menstrual blood is alkaline) indicates prophylactic therapy over several cycles.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this fungal disease is made by microscopic examination of material taken from the affected part of the vagina. Sometimes, the doctor can conclude that it is about Candida albicans infection by reviewing the characteristic of vagina appearance.Treatment
Given that antibiotics promote the growth of fungi, they are not used in the treatment. Antimycotic therapy is applied in the form of vaginal suppositories which are placed in the vagina and creams that are applied externally. Also, the therapy can be carried out by antifungal tablets. The symptoms usually very quickly disappear after the treatment.Proper hygiene of the vagina is also very important. It shouldn’t be washed with too strong antiseptic means which destroys the natural defensive barrier - normal bacterial flora and create the conditions for the development of fungal infection. It is enough to wash the genitals with water and appropriate low pH soap. Also, synthetic underwear and tight clothes should be avoided.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...