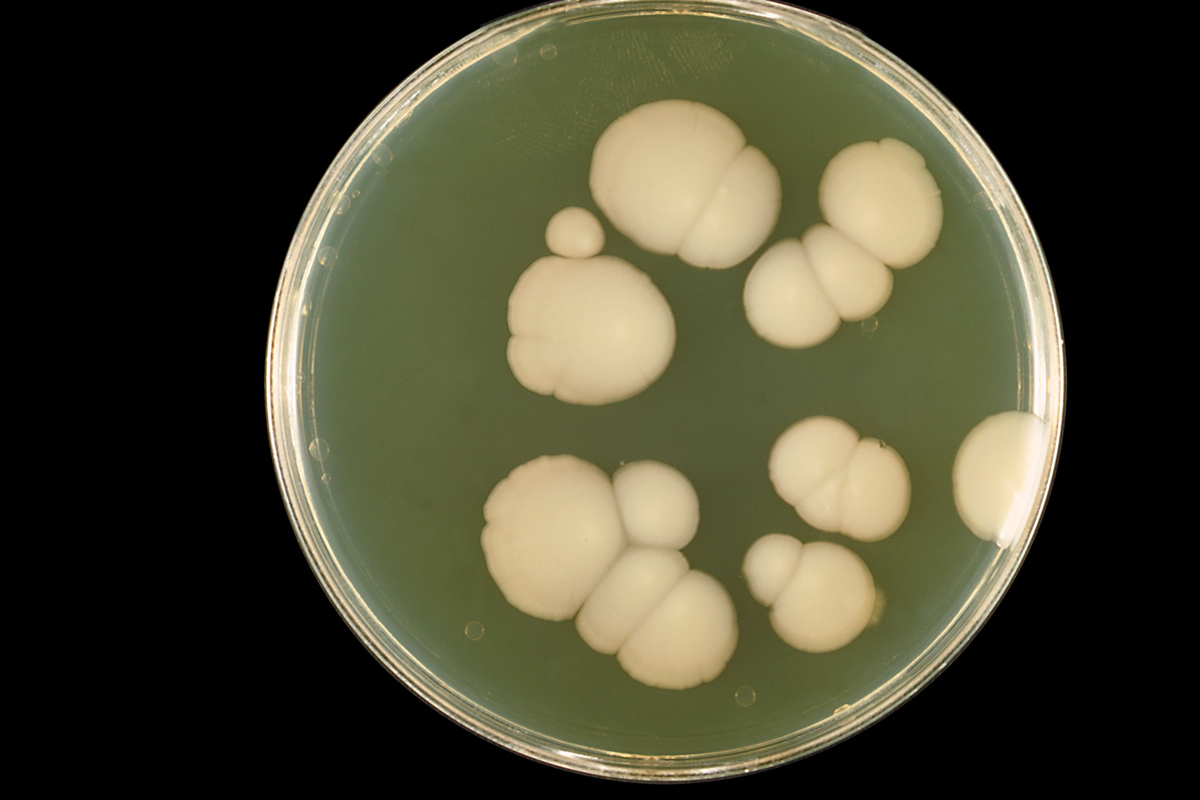
Candida is a genus of yeasts that normally inhabits the surfaces of the human body. Some Candida species, Candida albicans for example, can cause a disease in humans. The healthy immune system keeps the balance of various bacteria at the optimum level but, under the certain circumstances, the bacteria may overgrow and cause the infection. Yeast infections are most common in patients with a compromised immune system, such as people with chronic diseases like cancer, transplants and AIDS patients. Candida is normally found on the adult skin and the albicans species usually inhabit the flora of the mucous membranes of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and female genital tracts.
Candida infections
Overgrowth of some species of Candida can cause superficial infections in the mouth, also known as oropharyngeal candidiasis or oral thrush, and vulvovaginal candidiasis. Normally these conditions clear on their own but in immunocompromised patients they present a real threat since the candidiasis can become a systematic infection and, by spreading through the bloodstream, infect even the internal organs. It is estimated that Candida albicans lives in more than 80 percent of human population while showing no diverse effects. This infection may also affect the child’s diaper, spreading from the digestive tract.
Signs and symptoms of Candida infection
In most of the cases, the infection is completely superficial and characterized by local inflammation, redness, itching and general discomfort. This yeast infection most commonly causes vaginal irritation, also known as vaginitis. It can result in cottage cheese like discharge, itching and pain, accompanied with foul vaginal odor. This condition is very common and affects women of all ages.
Superficial yeast infection of the mouth, also known as oral thrush, usually manifests as thick white or cream-colored deposits on mucosal membranes in the oral cavity. The mouth is usually very much inflamed and the mucous layers are slightly raised. The whitish deposits are easy to scratch off, but they usually leave slight bleeding accompanied by burning sensation and general discomfort.
Unlike the superficial infections, systemic candidiasis is an infection of Candida albicans causing widespread disease and sepsis, invariably when host defenses are compromised.
Causes of Candida yeast infection
As already mentioned, the overgrowth of normally present Candida yeasts is limited by the healthy human immune system. Various factors may cause the Candida overgrowth in otherwise healthy individuals. Women may change their vaginal flora by using aggressive detergents or douches. Hormonal changes caused by pregnancy or the use or oral contraceptives, can also disturb the normal vaginal flora. Poor hygiene or involving in vaginal sex immediately and without cleansing after anal sex, is another significant risk factor. The use of antibiotics and underlying diabetes mellitus are also associated with risk of candidiasis.
Weakened immune system is also a significant predisposing factor for Candida yeast infection. Diseases tightly associated with candidiasis are HIV/AIDS, mononucleosis, cancer treatments, steroids, stress and nutrient deficiency.












_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...