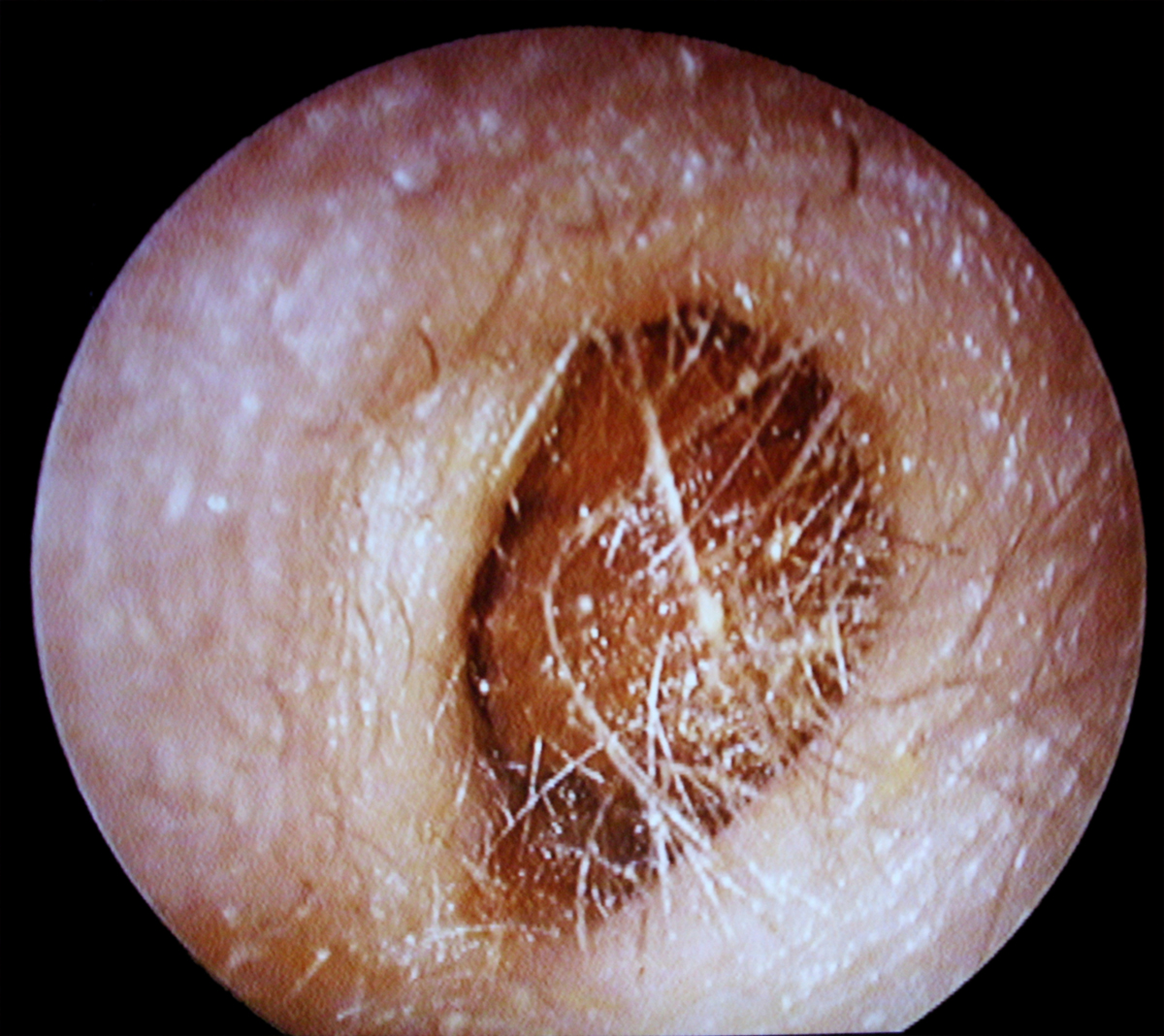
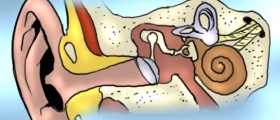
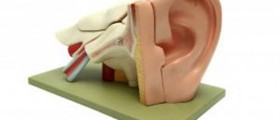
Cerumen is a medical term for earwax. It is produced by the wax glands normally found in the ears. This is a sticky yellowish substance with a specific purpose. Namely, it possesses lubricating, antibacterial and anti-fungal properties. It is essential in maintaining the proper moisture of the ear and traps foreign particles preventing them from entering deeper in the ear canal. Still, in spite of its function people consider cerumen dirty and regularly remove it from the outer ear canal.
Cerumen impaction is a condition in which cerumen builds up and blocks the ear canal. This occurs when accumulated cerumen hardens.
Causes of Cerumen Impaction
After being produced cerumen is carried to the opening of the ear by the movement of the outer layer of the skin that covers the outer ear canal. After reaching the opening of the ear this yellowish substance dries out and simply flakes off. This is a normal process of cerumen elimination from the body. The movement of cerumen and its elimination is enhanced by chewing. Still, in some cases (such as overproduction of cerumen) the ear may not be able to remove cerumen completely which eventually leads to its accumulation. Apart from overproduction of cerumen, cerumen impaction may be caused by frequent and inadequate use of cotton-tipped swabs and similar objects. They are used to remove cerumen from the ears. Inappropriate uses of cotton-tipped swabs may only push cerumen further inside the outer ear canal and add to the buildup. Cerumen impaction also affects people who use hearing aids or ear plugs, those with narrow/ twisted ear canal and it is common in people of old age.
Symptoms of Cerumen Impaction
Cerumen impaction typically features with partial loss of hearing and feeling of fullness in the affected ear. Furthermore, the accumulated cerumen may cause itching, ear pain, tinnitus, vertigo, cough and in some cases dizziness.
Treatment for Cerumen Impaction
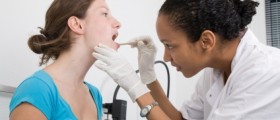
The very presence of impacted cerumen can be diagnosed by a simple examination of the outer ear canal. The condition is treated with irrigation and flushing the ear with lukewarm water. The doctor may use either syringe or other flushing instrument to remove impacted cerumen. If this procedure fails cerumen is first treated with cerumenolytic solution which will soften the impacted mass. Softening of a hard cerumen is successfully achieved by several cerumenolytic substances such as mineral oil, baby oil, peroxide based ear drops, saline solution and glycerin. After ear irrigation the doctor applies antibiotic ear drops. They are administered to prevent any kind of infection. Ear irrigation is never performed in case the eardrum is perforated or a patient has a history of otitis media. And finally, if irrigation fails even though a cerumenolytic solution has been applied the doctor will remove the impacted cerumen with an instrument called a curette or with the assistance of a vacuum device.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...