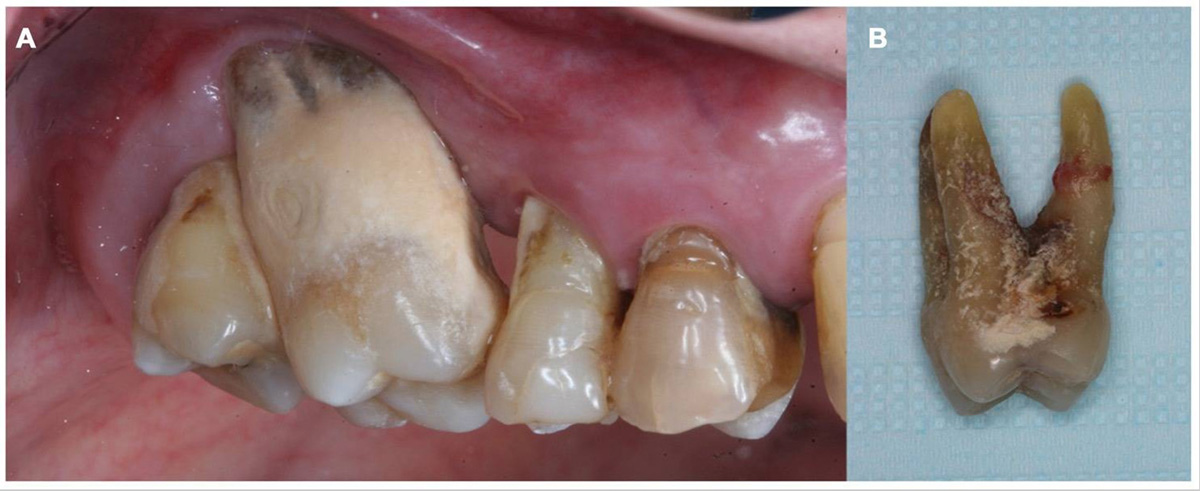
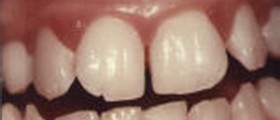
Gingival recession is recognized by shrinking gums so that the roots of the teeth are being exposed. Untreated it may cause exposed roots to become tender or infected, causing great pain to the patient. Recession of gingiva usually occurs in patients that don't have periodontitis or gum disease. However, gum infection and inflammation may take place after the recession as a resulting complication. Recession often happens with no obvious signs of periodontitis - looseness of teeth, bleeding gums, redness. Cause of recession is the lack of the Attached Gingiva - thick tissue situated on the borders where gums meet teeth. This lack in tissue isn't caused by patient neglect, patients are usually predisposed for recession problems.
Symptoms of gum recession are:
Teeth sensitive to temperature changes, sweet, sour or spicy food.Teeth appear longer The roots of the tooth become visibleTooth changes colorGrowing spaces between neethThere are several causes of gingival recession:
Prominent roots - growing tooth is surrounded by a layer of bone tissue. In normal conditions, a gum tissue forms to cover the bone, but if the developing bone doesn't have the normal thickness or if it is absent on one side of the tooth, the gum tissue formed this way will be thin and sensitive, not able to resist pressure of chewing food hitting the gums or even proper brushing.
Muscle attachments - at the base of the recession is a muscle attachment that creates tension on the gum tissue and thus causes recession. Those muscles give us the ability to chew and make facial expressions. Sometimes these attachments are placed right on the margin where gums meet the teeth, or they are extremely large, so they provoke the recession.
Orthodontic Associated Recession - occurs in some patients undergoing orthodontic treatment. In most cases the orthodontist need some extra space in the jaw to move teeth, and often the only way to align teeth may be if the roots of the teeth are made more prominent. Teeth extraction may make some extra space, but not many of patients are willing to accept this method.
Brushing trauma - overly agressive brushing with a hard brush causes physical damage to the gums. The enamel at the gum line thus wears away. The same undesirable effect may occur if we brush our teeth too often.
Trauma from Removable partial denture - patients who wear it are predisposed for the gingival recession, usually on the inner side of the lower teeth.


,-Don't-Ignore-Receding-Gums_f_280x120.jpg)







_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...