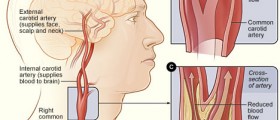
Whatis carotid artery?
Carotidartery is a blood vessel through which blood rich with oxygen andnutrients reaches the brain. Nerve cells in the brain are very power-hungry in terms of oxygen and glucose consumption, and even a slightlack of either of these can cause consequences that range from mildto severe. Prolonged lack of oxygen supply to the brain (a matter ofminutes) causes death. Carotid artery has two branches that rung upthe neck and supply blood to both the corresponding hemisphere of thebrain and the face. Pulse on the neck is checked on the carotidartery and movie vampires like to bite in it.
Whatcan go wrong with carotid artery?
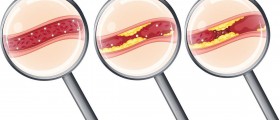
Besideinjury or trauma, carotid artery can become blocked. This happensbecause of development of plaque. Partial blockage of carotid arteryis referred to as artery stenosis. This condition leads to decreasedflow of blood to the brain and can have consequences such as stroke.This condition, if it has already occurred, is fixed by means ofsurgical procedure.
Surgicalprocedure for repair of blocked carotid artery
Thereare two types of surgical procedures for repair of carotid arteryblockage. The first procedure is carotid endarterectomy.
Thisprocedure is performed under general anesthesia. An incision is madein the skin above the artery to expose it. Then a catheter (a small,elastic pipe made of plastic that does not irritate tissue) is placedbeside the artery and the blood is re-routed through it so that thereis uninterrupted flow of the blood to the brain. The artery is thenopened, cleaned up, and stitched. Functioning of both the heart andthe brain are closely monitored during the procedure, to ensureprompt response to possible complications.
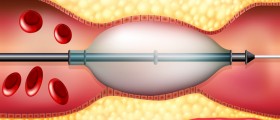
Theother procedure is known as CAS, or carotid angioplasty and stenting. In here, a catheter and a guiding wire are used to lead the second,small catheter to the location of the blockage. This small catheteris equipped with a small balloon that will be placed in the blockageand then blown (of course, sizes and volumes discussed arecorresponding to the diameters of the arteries involved) to expand.Once expanded, the balloon will open up the blocked artery. A stent(a thin tube inserted into the artery to hold it open orremove a blockage), if it is used, is placed at the site of theblockage and left in there,while the balloon is removed.
Risks
Thisprocedure is dealing with very sensitive structures and possiblerisks are serious and include stroke, brain damage, nerve injury andothers.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...