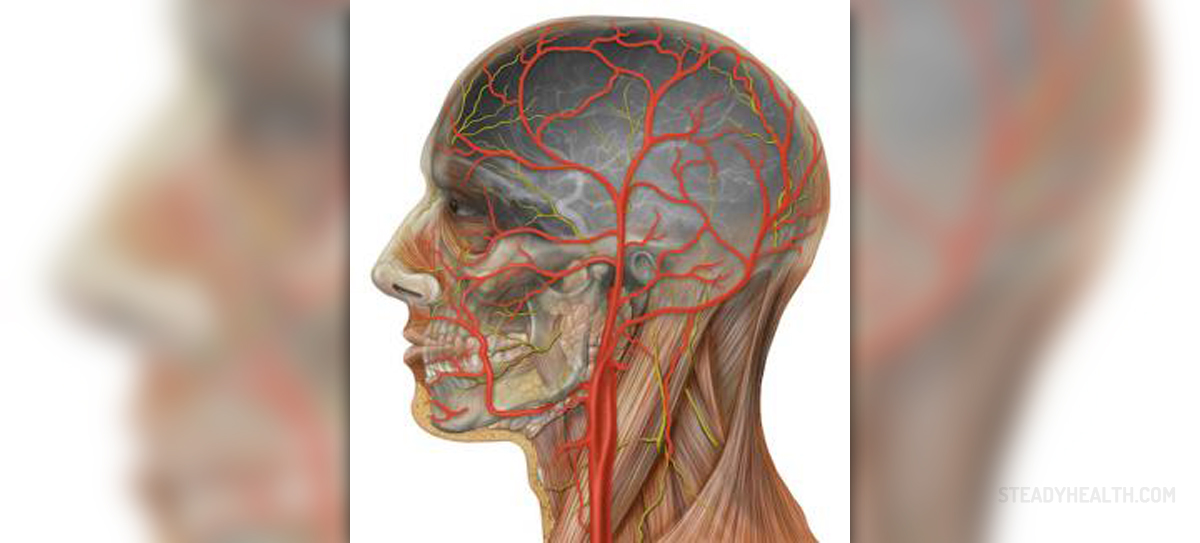
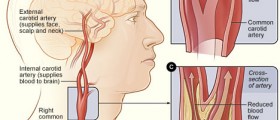
The carotid artery also known as the common carotid artery is the main blood vessel which supplies the head and the neck with oxygen and other necessary nutrients. This artery divides into the external and internal carotid artery. These two arteries separate form the common carotid artery in the neck. Blockage of these two arteries represents a serious medical condition and is one of the major contributors to stroke.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Blockage
The problem related to carotid artery blockage is that the disease is asymptomatic in majority of patients. Blockage may be accidentally found during examination and test performed for other purposes. So the blockage may exist many years and the patient does not have to be aware of its presence.
If there are any symptoms, they are usually very subtle. Many patients become familiar with the presence of the carotid artery blockage once they have suffered TIA, stroke or heart attack.
Patients who do have certain symptoms may complain about a hissing sound either in ear with each heartbeat, temporary loss of vision or hearing, very intensive headaches, loss of motor coordination, problems with speaking and slurring of words, sudden numbness of one or both sides of the face, arms or legs.
If you suspect that you or someone you know is having a stroke, you should call an ambulance right away. Warning signs of a stroke can be remembered with the abbreviation FAST:
- Face,
- Arm,
- Speech,
- Time.
Luckily, symptoms and signs of TIA are transitory and are actually an introduction to stroke. Once they occur patients can be treated and potential stroke can be prevented.
Diagnosing Carotid Artery Blockage
The diagnosis can be set after routine examination of the patient, during examination in other purposes of after the patient has suffered mini stroke. By using a stethoscope the doctor can hear and identify the unusual sounds in the carotid artery which occur due to the blockage. Further examination includes standard ultrasound of the carotid arteries and Doppler ultrasound of carotid arteries. The patient may even undergo a cerebral angiogram.
If there are complications due to the blockage one may require additional tests and examinations and specific imaging methods in order to establish the damage to the brain tissue.
Treatment for Carotid Artery Blockage
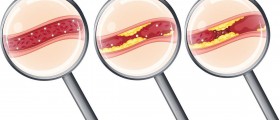
The treatment depends on the degree of the blockage and the symptoms of the disease. If the blockage is not so intensive the patients are commonly prescribed blood thinners which prevent blood clotting. Severe blockage is treated surgically. The artery is cut open and the plaque is removed. Another surgical procedure applied in carotid artery blockage is carotid angioplasty.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...