Many people have experienced calf muscle cramps, which can last from a couple of seconds to a couple of minutes, thus being very painful. Both men and women can experience spasms in the calf muscles that cross two joints. A cramp is usually described as a sustained spasm with an involuntary contraction and pain. Various ways can help you release the calf muscle cramp, but in most cases, relaxation, massage, and stretching are most helpful.
Causes of Calf Muscle Cramps
There are a lot of causes of the calf muscle cramps. You can have calf muscle cramps because you changed your everyday activities; for example, if you start playing some sports like swimming, tennis, or mountain climbing, it can affect the muscles that are not ready for that kind of strain. Disturbed muscle control or coordination can also cause calf muscle cramps. Changed salt levels that are caused by the low or high potassium or sodium levels can cause the leg cramps as well.
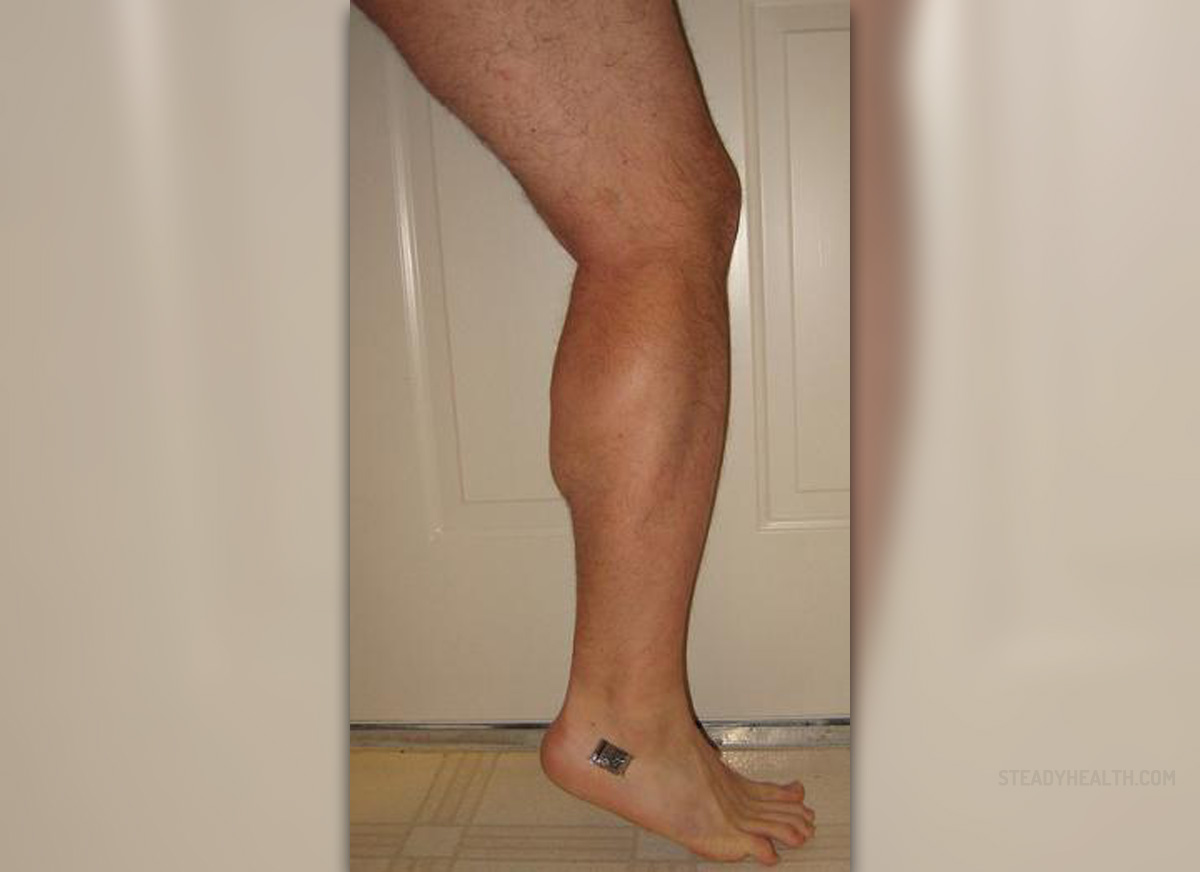
Vitamin deficiency or the additional weight of the baby on the leg and feet muscles can cause calf muscle cramps. You need to exercise regularly and eat healthy food to avoid this condition, which can also affect some well-trained athletes due to the overstraining of the muscles resulting in them becoming fatigued. If you don`t drink sufficient amounts of water, you may experience calf muscle cramps.
Releasing environmental toxins can also be one of the causes, but people who suffer from diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, renal failure, diabetes, liver cirrhosis, or cancer may experience fatigue followed by calf muscle cramps. Peripheral vascular disease is known to have symptoms like narrowed leg arteries or poor blood circulation, which can lead to this condition.
People who are overweight or obese and do nothing but sit in one position and eat are prone to have calf muscle cramps. Some suffer from plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendonitis and they may experience the pain in the leg followed by the calf muscle cramps. Other causes of calf muscle cramps include hyper-flexible joints, cardiovascular exercises, intake of alcohol, uncomfortable footwear, foot or leg injuries, and flat feet. Some medications can cause the calf muscle cramps as their side effect.
Treatment
There are several helpful tips on how to prevent calf muscle cramps, but there are also a couple of treatments for it. Various exercises, massages, and stretching techniques can help you reduce the pain in the muscle, but you should try to relax your leg as much as possible. One very helpful advice in case you experience calf muscle cramps is to stretch your leg and hold it with your hands until it disappears, after which you can massage the leg for a couple of minutes.
Some people apply the elastic bandage to the affected area to reduce the pain of the calf muscle cramps. It is important to drink a lot of liquids like milk, juices, and water to prevent yourself from having calf muscle cramps. Certain medications, oil massages, a balanced diet, or an ice pack can really help in reducing the pain and muscle fatigue.
- Nocturnal leg cramps usually occur in the calf or foot during sleep, and often results in sleep disruption. It is diagnosed clinically when the patient meets all three of the diagnostic criteria by American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM): (1) painful sensation in the leg associated with sudden, involuntary muscle contraction; (2) painful muscle contractions that occur during time in bed, although it can occur when one is awake or asleep; and (3) pain that is relieved by forceful stretching of the affected muscles.
- It is most prevalent in the older age groups, although it has been reported in 7% of children and adolescents. Older and less physically active adults are more likely to have shortened muscle length, which poses as a risk factor. Most nocturnal leg cramps are idiopathic and there is currently no consensus about the aetiology. No investigations are necessary for nocturnal leg cramps unless history and physical examination suggest an underlying cause.
- Vascular claudication refers to muscular pain that develops with exercise as a result of ischaemia and is quickly relieved by rest. It indicates peripheral arterial disease (PAD), where arteries distal to the aortic arch are narrowed secondary to atherosclerosis.
- Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) is a reversible increase in intramuscular pressure within an inelastic fascial compartment. Typically, patients with CECS can present with calf cramps with pain in a specific location in the lower extremity, and may be associated with altered sensation and weakness. These symptoms occur predictably with increasing pain over the specific region after a specific time of exercise, and are relieved within minutes to hours of stopping the aggravating activity.
- Neurogenic claudication, also known as pseudo-claudication, occurs in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. It can be diagnosed based on a history of typical symptoms, physical examination and radiographic imaging. Typical features include leg cramps, buttock and back pain with walking downhill and/or lumbar extension, which improve with spinal flexion or upon sitting.
- Exercise-associated muscle cramps (EAMC) occur during or soon after physical activity in healthy individuals with no underlying medical pathology. Clinically, they can present with acute cramps, stiffness, and soreness that can last from a few minutes to several days.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...