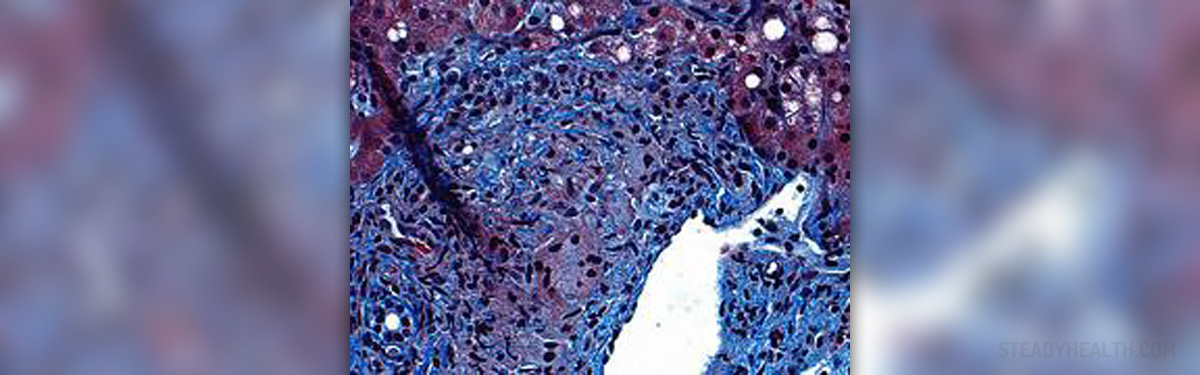
What is autoimmune hepatitis?
An autoimmune disease is basically a disease caused by the immune system of the body that turned around and started attacking the healthy cells. The immune system has the purpose of fighting all adverse factors and agents that could harm the body, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc. the sudden change in the routine of the system is called autoimmunity.
The list of autoimmune diseases is, unfortunately, very long, and autoimmune hepatitis is just one of those diseases on the list. Hepatitis is a disease that affects the liver, causing inflammation. In autoimmune hepatitis or chronic autoimmune hepatitis, the immune system starts attacking the healthy liver cells, triggering the inflammation.
Autoimmune hepatitis is mostly genetic and it affects women more than men. There are two types, type 1 and type 2 autoimmune hepatitis, and type 1 is much more common.
Symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis
Like in any other disease, the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are best if recognized and addressed as early as possible, so the disease can be treated more efficiently. The symptoms vary from person to person but they commonly include fatigue, exhaustion and abdominal pain, which results from the liver inflammation. Other symptoms include jaundice, in which the skin turns yellowish and it is the tell-tale sign that there is something wrong with the liver, nausea, vomiting, joint pain, bloating, dark-colored urine and loss of appetite. In women, autoimmune hepatitis also causes problems with the menstrual cycle. Enlarged liver and apparent blood vessels on the skin are also symptoms of this disease, although they are much less common. In some people, autoimmune hepatitis also causes fluid retention in the abdominal region and frequent blackouts.
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis can be fatal and in most cases it can never be cured completely. However, if it is diagnosed early on, there is a great chance that proper treatment will be able to control it, even to a major extent.
Medications used to treat autoimmune diseases are called imunosuppressants and their purpose is to calm down an overactive immune system. These medications are very effective for type 1 autoimmune hepatitis, but unfortunately, the type 2 does not respond well to this therapy.
After a few months of treatment with immunosuppresants, the symptoms will most likely disappear completely. However, it is very important to stay in touch with the doctor who treated the disease, especially if any of the signs reappear, because autoimmune hepatitis tends to reoccur. Blood and laboratory tests need to be repeated on a regular basis because it may seem that the disease is cured but it can come back after several years.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...