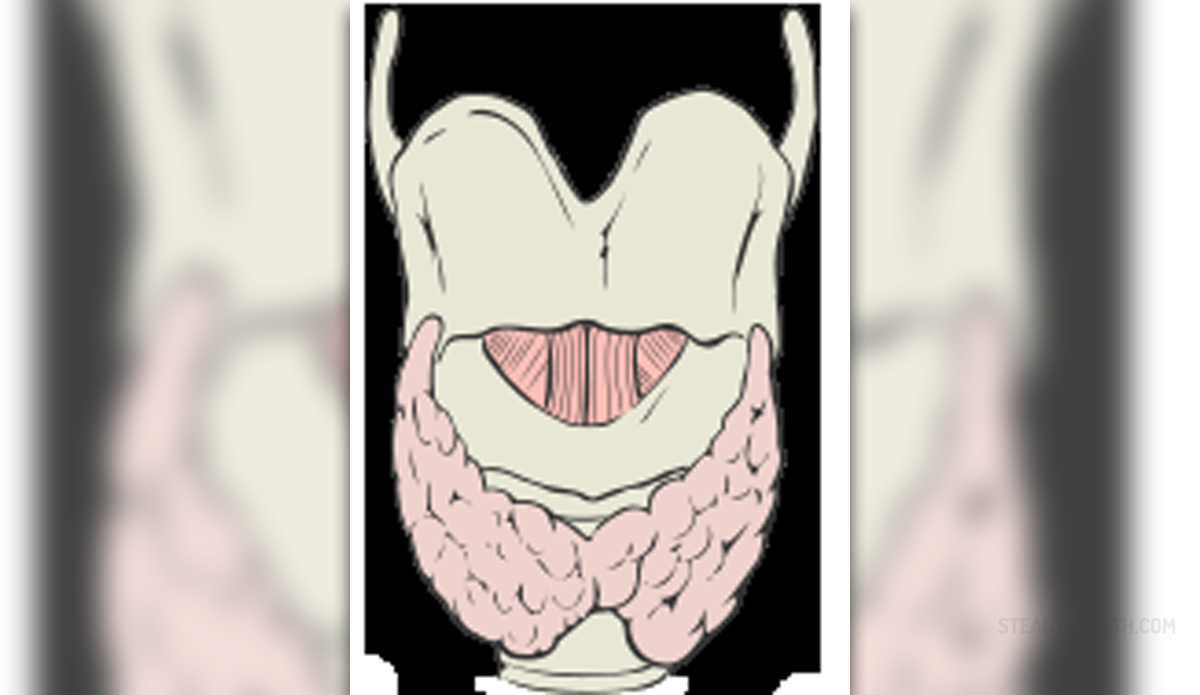
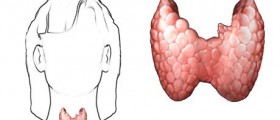
Diseases of the thyroid gland are usually caused by autoimmunity and occur when the immune system of an affected person attacks and destroys its thyroid. Genetics is found to be a risk factor for development of autoimmune thyroid disease. Response of an individual's immune system to different triggers also plays a role in developing an autoimmune disease. The immune system is additionally affected by aging, chronic stress, hormonal imbalance and pregnancy and these conditions too can contribute to autoimmune diseases.
Causes of Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
Any autoimmune disease is primarily caused by antibodies that are produced by the body's immune system, which attacks and damages body's healthy body tissue. In case of autoimmune thyroid disease, the immune system produces antibodies that attack the thyroid gland. This causes the gland to produce excess thyroid hormones which leads to enlargement of the gland. This condition is known as Grave's disease. Overproduction of thyroid hormones, a condition known as hyperthyroidism, can further aggravate a sufferer's health.
What exactly causes the immune system to create these abnormal antibodies is still unexplained. Scientists have not yet identified the responsible gene for autoimmune thyroid disease but several genetic as well as environmental factors are recognized as triggers for the disease. These include: stress, viral infections, exposure to toxins, use of steroids, iodine intake and female sex hormones.
Hashimoto's disease is another autoimmune thyroid disease characterized by an underactive thyroid gland. Damage to the thyroid due to autoimmunity leads to decrease of thyroid hormone level in the blood, hormonal imbalance and inflammation of the gland. Underactive thyroid gland is a condition known as hypothyroidism and it can lead to other health complications such as goiter, poor memory, depression and others.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Thyroid DiseaseGrave's disease causes symptoms of an overactive thyroid gland or hyperthyroidism. The symptoms include: hypertension, arrhythmia, insomnia, muscle weakness, unusual weight loss, irritability, increased appetite, protrusion of eyes, sensitivity to heat, excess sweating, diarrhea, brittle hair and enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Signs and symptoms of Hashimoto's disease are similar to those of hypothyroidism. The disease is typically accompanied with fatigue, depression, joint pain, swelling of joints, constipation, increased cholesterol level, loss of appetite, unexplained weight gain, cold intolerance and dry skin.
Treatment for Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
Grave's disease is treated with beta blockers, anti-thyroid medications and radioactive iodine. Surgical removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) is an option only if a patient does not respond to medication treatment and radioactive iodine therapy.
Hashimoto's disease is treated by a replacement therapy with synthetic thyroid hormone. Certain medications, supplements and different naturopathy treatments can also help in treatment of Hashimoto's disease and promote the effect of synthetic hormones.




-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)
-And-Children-16-Warning-Signs-And-Symptoms_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...