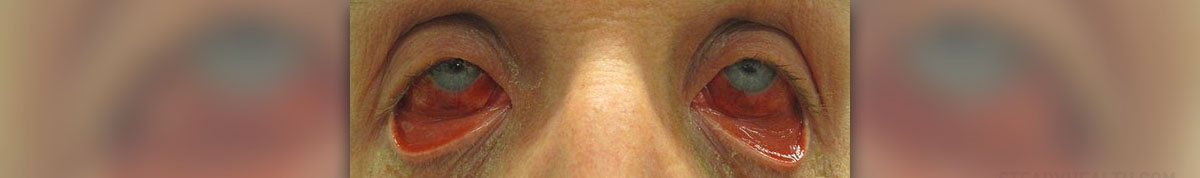
Fulminant hepatic failure is rapid and quite severe impairment of liver functions due to necrosis of liver cells (hepatocytes) in people whom the liver previously has not been damaged. In adults the condition is generally accompanied by encephalopathy while in children this medical problem may be absent, occur late or stay unrecognized. In children the main care is associated with problems regarding coagulopathy.
The cause of pediatric fulminant hepatic failure may stay unidentified. Such children typically develop jaundice as well as some additional symptoms and signs of liver failure and their level of consciousness rapidly deteriorates. The disease soon progresses into cerebral edema and coma.
Causes of Fulminant Hepatic Failure
The onset of the condition is associated with exposure to an agent that causes immediate damage to liver cells. The exact cause most commonly remains undiagnosed. It is believed that hepatic encephalopathy develops due to accumulation of neurotoxic and neuroactive substances due to hepatic failure. The brain damage may result from ammonia, false neurotransmitters as well as some substances taken orally (hepatotoxic medications).
In children fulminant hepatic failure is frequently induced by different infectious diseases, hepatotoxic drugs, certain toxins as well as metabolic disorders or ischemia.
Infectious diseases that may be blamed for the condition include hepatitis caused by different hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D or E). It is also possible to develop fulminant hepatic failure after infection with other viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, Citomegalvirus, Varicella-zoster virus etc.
Hepatotoxic drugs that may induce severe and rapid damage to hepatocytes are acetaminophen, paracetamol, chlorinated hydrocarbons, salicylates, isoniazid, intravenous tetracycline and sodium valproate.
Metabolic disorders such as tyrosinemia, hereditary fructose intolerance, galactosemia and neonatal hemochromatosis are all potential causes of fulminant hepatic failure.
Even medical conditions like cardiomyopathy, sepsis, shock, cyanotic heart disease or severe asphyxia may induce damage to the liver and subsequent medical issues.
And finally, fulminant hepatic failure may be closely related to Hodgkin disease, leukemic infiltration as well as autoimmune hepatitis.
Treatment for Fulminant Hepatic Failure
After many diagnostic tests, exams and procedures doctors may evaluate the etiology, severity as well as prognosis of the condition. Liver biopsy is required in many cases.
Patients need to receive symptomatic treatment and life support. The treatment goes towards the specific cause in case it has been identified. Patients are usually hospitalized and stay in an intensive care unit. Fulminant necrosis leads to permanent damage and the only way to help such patients is to provide them a liver transplant.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...