
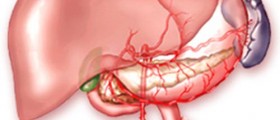
Hepatitis is actually liver inflammation, usually caused by viruses called hepatitis A and B. These viruses mainly affect liver cells, causing their destruction. According to the duration of the liver inflammation, we can differentiate acute and chronic hepatitis. Acute hepatitis lasts for less than 6 months, while chronic hepatitis is the disease lasting for more than 6 months of time.
Acute Hepatitis Causes
As mentioned, hepatitis viruses are usually responsible for hepatitis and there hepatitis A, B, C, D and E viruses. Besides these, viral diseases caused by cytomegalovirus and glandular fever may also cause hepatitis, as well as some amebic or serious bacterial infections. Sometimes, alcohol, fungal toxins (toadstool toxin) and medications such as halothane or paracetamol may also be identified as the cause of liver inflammation.
People may get hepatitis contracting the viral infection or by exposure to toxins, certain drugs or alcohol. Halothane causes hepatitis due to abnormal reaction of the liver to normal dose of the drug, while paracetamol-related hepatitis is usually provoked by drug overdose.What Are Symptoms of Acute Hepatitis?
Patients diagnosed with acute hepatitis might be asymptomatic (have no symptoms of the disease), while children in most cases experience very mild symptoms. In early days of the disease, patients may experience nausea, poor appetite, taste changes, as well as slight fever, ill feeling and tiredness. Their muscles and joints might be painful and they could have headaches. Skin rash is also frequently present in these patients. Enlarged liver due to inflammation may be responsible for the pressure or pain located below the right ribs, that hepatitis patients have reported quite often.
Further progression of the disease is known as jaundiced phase, where the patients usually experience yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and the sclera (white part) of the eyes. At the same time, previous symptoms usually disappear. Additionally, there are some changes in the color of urine (darkening) and stool (lighter stool). Recovery phase of hepatitis is usually followed by tiredness which may last for several weeks in some patients.Risk, Prevention and Treatment Measures
People in high risk groups and those who already have hepatitis symptoms are at risk to develop hepatitis. Increased risk is also noticed in people who have hepatitis running in the family.
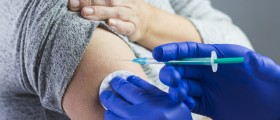
Prevention measures involve avoidance of hepatitis virus infections and vaccination against hepatitis A and B in high risk population. Limitation of alcohol intake is also possible and desirable method of prevention. Acute viral hepatitis generally doesn’t require any therapy.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...