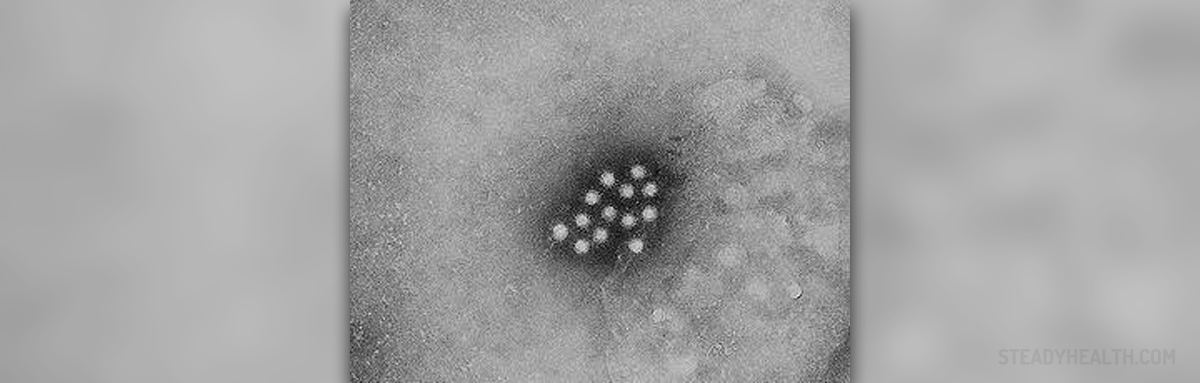
Hepatitis A is inflammation of the liver caused by hepatitis virus A, a RNA virus and a member of genus hepatovirus, family Picornaviridae. The infection caused by hepatitis A is transmitted via the fecal-oral route after consumption of contaminated food or water or after being in contact with infected person. Once the virus is contracted, there is an incubation period of approximately 28 days (2-6 weeks) and then symptoms and signs of liver inflammation start to occur.
Hepatitis A in Children and Its Transmission
As far as developing countries and areas with poor hygiene standards are concerned, this viral infection is basically contracted during childhood. The number of newly diagnosed cases drops in regions where income rises and the amount of clean water increases. It is estimated that around 90% of infected children develop asymptomatic infection. Once the infection is gone, the person is immune to the virus for the rest of his/her life. In developed countries like the United States hepatitis A generally affects young adults who contract the virus either via contact with the infected individuals or during trips to endemic countries.
The virus is easily contracted in conditions of poor sanitation and overcrowding. Even though the major route for transmission of the virus is fecal-oral route, hepatitis A virus can be also transmitted by parenteral route. The infected people start shedding the virus even before they actually develop clear symptoms of infection and remain infectious for 10 days after the first symptoms develop.
As for the virus, it shows resistance towards detergent, acid solvents, drying and cannot be destroyed at temperatures below 60°C. As a matter of fact it can easily survive for months. Successful elimination of the virus is achieved with chlorine treatment of drinking water, UV radiation and use of several more substances and disinfectants.
Hepatitis A Symptoms and Signs in Children
Clinical characteristics of hepatitis A in children are actually the same as the ones in adults. Fortunately, the infection is self-limited and never progresses into chronic liver inflammation. In spite of the mentioned, hepatitis A may sometimes cause a disease relapse with symptoms and signs reoccurring within the period of 6 months after the initial infection. Children either develop symptoms and signs of liver inflammation or overcome the illness without any trace of infection (asymptomatic patients).
After the incubation period, hepatitis A infection initially causes fatigue and fever. Patients soon start to complain about abdominal pain, generally lose their appetite and feel nauseated. Vomiting occurs as well. Within a day or two, due to bilirubin build-up the skin of the affected individual turns yellow. Even the whites of the eye become yellow. The excess of bilirubin is additionally excreted via urine. Because of that the color of urine becomes dark amber. On the other hand, lack of bilirubin in feces gives it the color of clay. The skin may be itchy and one may additionally report muscle ache. Prolonged vomiting is associated with dehydration and accompanying health issues like confusion and inability of one to concentrate, rapid heartbeat, headache, decrease urination and irritability.
Hepatitis A Statistical Data
The infection affects tens of millions of people around the world per year. As for the United States, statistical data confirm that hepatitis A affected 30,000 people in 1997, and 270,000 people were infected within the period of 20 years (1980-2000). The most severe outbreak occurred in 2003 in north-eastern Ohio and western Pennsylvania where infection affected around 640 people. There were 4 lethal outcomes. The official number of hepatitis A cases is much lower than the actual number of infected individuals because most of them remain asymptomatic and are not actually confirmed to be suffering from this infectious disease. The incidence of the infection is reduced with vaccination of all individuals who travel to endemic countries. Routine vaccination is also performed in children and people at risk for the disease.
Treatment for Hepatitis A
There are no medications which will fight off the virus and eliminate it from the body. So treatment for hepatitis A is basically symptomatic and includes proper rest, a light diet which does not include fatty foods and alcohol. Patients must be well hydrated and they will soon recover completely.
If there is a need, one may receive analgesics (abdominal pain), antipyretics(fever), and in rare cases the person will receive immune globulins (BayGam 15-18% IG).
Hepatitis A Prevention and Prognosis
The best protection is achieved with the vaccine. However, the infection can be also prevented by good hygiene and sanitation. By washing hands thoroughly with warm water and soap, one may prevent further shedding of the virus and contamination of food he/she manipulates with. Also, proper sanitation will not allow contamination of drinking water with the virus.
The prognosis is very good and lethal outcome is reported only in older individuals (those aged 50 and older). These patients die due to acute liver failure but this catastrophic complication basically affects people who have already had damaged liver.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...