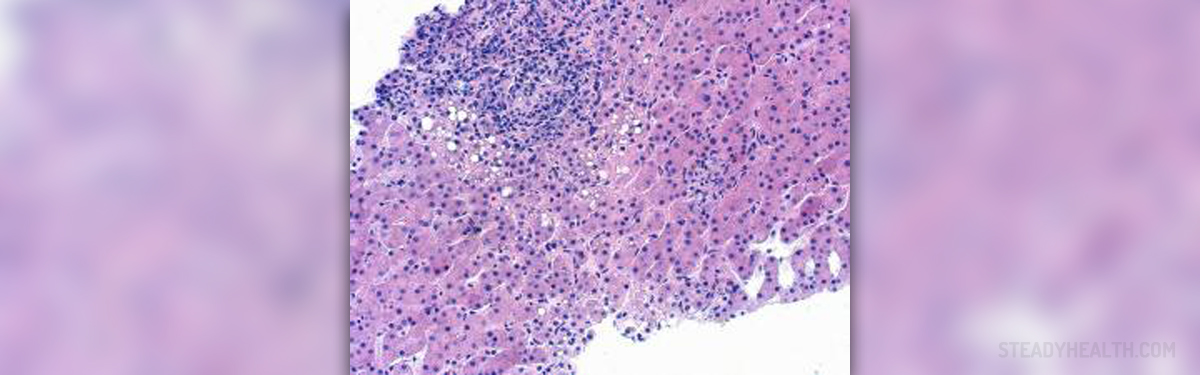
Hepatitis is a liver disease. Person with hepatitis has inflamed liver. Causes of hepatitis are toxic agents, medications or viruses. There is viral and non-viral hepatitis. Viral hepatitis can be chronic or acute. Chronic viral hepatitis affects slowly and has long-lasting symptoms. Acute viral hepatitis affects rapidly, has very severe symptoms and it lasts for short periods of time.
Viral hepatitis is divided in at least 5 types: hepatitis C, hepatitis E, hepatitis D, hepatitis B, hepatitis A.
Hepatitis B is the most serious of all types of hepatitis. It is transmitted by blood transfusion or by sexual relations. Also, it can be transmitted if you get in contact with blood of affected person, for example, needle and razor sharing, cuts, piercing tools or open sores. This type of hepatitis affected mother can pass to baby at birth. Hepatitis B is usually acute disease but about 10% of affected persons have chronic hepatitis B. Chronic hepatitis B can progress in liver cancer or cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is liver disease which damages its cells. This type is formally called serum hepatitis.
Hepatitis C is most commonly chronic viral disease. About 75% of affected people has chronic hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis C can cause cirrhosis. This type most commonly passes from affected person to other persons by blood contact, contaminated needles or blood transfusion. Also, this type can be transmitted from mother to baby at birth or by sexual relations.Hepatitis A is acute disease. It usually affects children in developing world. In developed world hepatitis A can affect people of all ages. Hepatitis A is transmitted by cooking utensils or someone else’s fingers, drinking water, raw shellfish or by affected person’s faces, contaminating foods. This type of hepatitis is formally called infectious hepatitis.Hepatitis E is acute disease and it is most commonly found in the region of Indian Ocean. Hepatitis D can be and acute and chronic disease. It is most commonly found in intravenous drug addicts. They carry virus of hepatitis B.
Non-viral hepatitis is divided in four types: autoimmune hepatitis, granulomatous hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis and toxic/drug induced hepatitis.Autoimmune hepatitis is when your own body attacks your liver.Granulomatous hepatitis is abnormal collection of blood cells in the liver. Alcoholic hepatitis affects people who drink excessively or it can affect people who misuse alcohol for several decades.
Toxic/drug induced hepatitis can be caused by medications or toxins. Medications which can cause this type of hepatitis are chlorpromazine, erithromicine, anabolic steroids, methyldopa, oral contraceptives and isoniazid. Toxins causing this hepatitis are vinyl chloride, poisonous mushrooms and carbon tetrachloride.
Symptoms of hepatitis are loss of appetite, nausea, fatigue, vomiting, mild fever, diarrhea, joints or muscle aches and pain in stomach. These symptoms are not serious and they occur in first acute phase. But is possible that this phase of hepatitis progress rapidly and causes death.
Some additional symptoms occur if person’s condition getting worse such as: hives, dark urine, itching, yellow mucous membranes, eye-whites and skin, stools have light colour and can have pus.
Symptoms such as dizziness, circulation problems, headache and drowsiness have only people with toxic/drug-induced hepatitis.
Only people with alcoholic hepatitis have enlarged spleen.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...