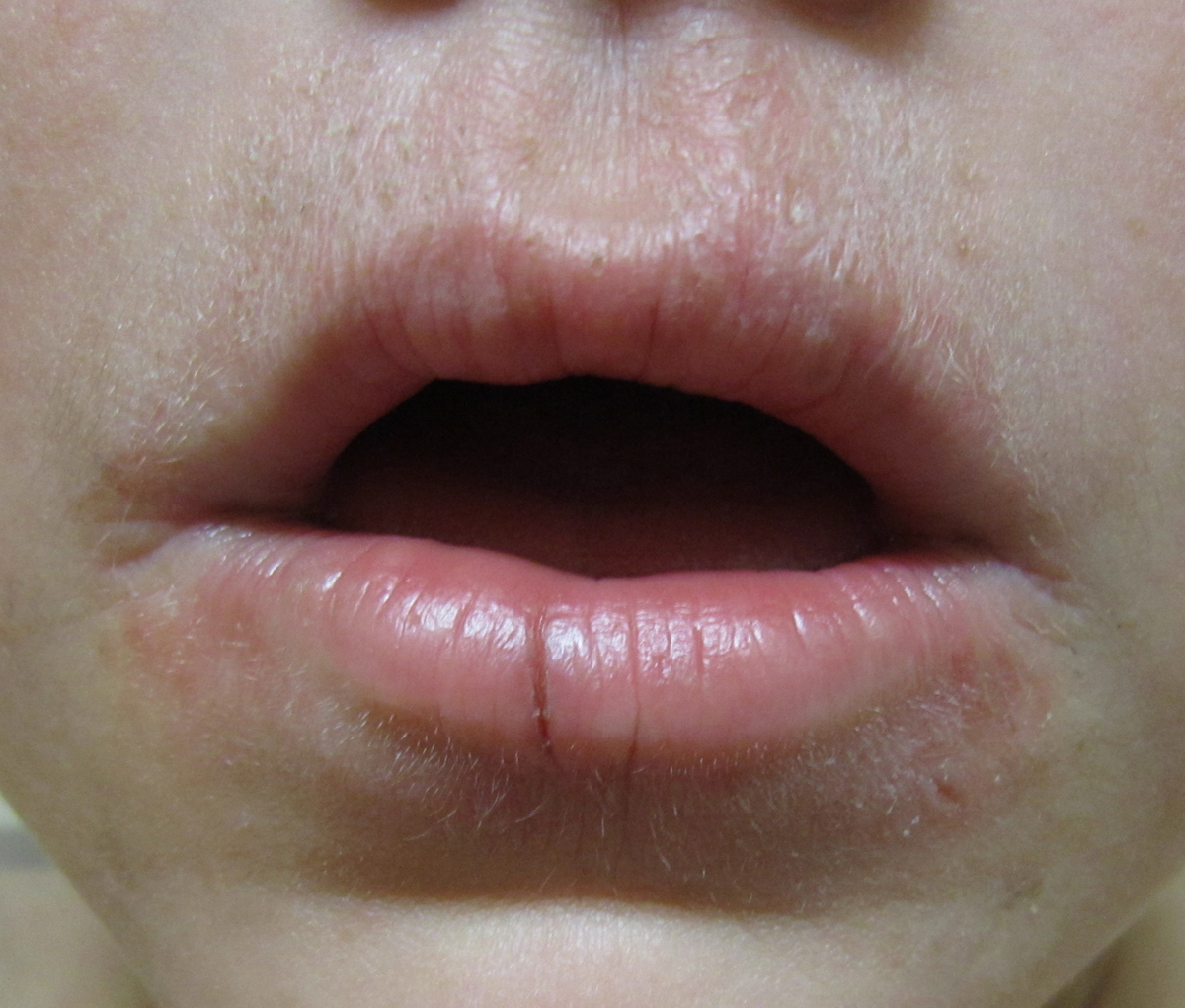
Actinic cheilitis is the same condition as actinic keratosis but the only difference is that actinic keratosis affects the skin while in actinic cheilitis specific changes occur on the lips. This is considered a precancerous lesion and may eventually transform into squamous cell carcinoma. The specific change on the lips is in a form of thick whitish discoloration and it typically develops at the border of the lip and skin. This lesion becomes scaly and indurated if left untreated. It is painless and persistent. Actinic cheilitis predominantly affects older men and is more frequent among people with light complexion and those with a history of chronic and excessive exposure to the Sun.
Causes of Actinic Cheilitis
Excessive and chronic exposure to the Sun and its harmful ultraviolet rays is in general the leading cause of actinic cheilitis. Fair-skinned people are much more susceptible to actinic cheilitis due to low percentage of melanin in the skin. Some scientists believe there are several more contributing factors. They may accelerate the process of transformation of the initial skin lesions into an aggressive form of the disease. They include use of tobacco and other irritation of the lips caused by a variety of physical and chemical factors.
Treatment for Actinic Cheilitis
Minor lesions can be successfully treated with 5-fluorouracil. This medication is applied topically and it can efficiently block DNA synthesis and stop the multiplication of abnormal cells. The treatment lasts from two weeks to a month depending on the size of the lesion. In initial phase of the treatment patients may complain about inflammation of the treated area accompanied by redness, burning sensation and erosion of the lip lesion. It is estimated that approximately 50% of patients respond to this treatment modality. One more medication with similarly good results is imiouimod. This is a very powerful immune response modifier. Apart for treating visible lesions this medication is also effective in unmasking of the hidden lesions this way making them visible and easier to treat.
There are several more treatment options for people suffering from actinic cheilitis. Surgical removal of the lip lesion includes cryosurgery and electrosurgery. These two approaches are performed in patients with small lip lesions. Cryosurgery includes application of liquid nitrogen while in electrosurgery the lesions are resected with electrocauter. Furthermore, actinic cheilitis can be treated with scalpel vermillionectomy, chemical peel and carbon dioxide vaporization. All the previously mentioned techniques destroy the affected epithelium and cause edema, pain and prolong the process of healing. However, they significantly reduce the chance of recurrence of the disease.
No matter what treatment modality is chosen it is essential to treat actinic cheilitis as soon as possible and properly and this way prevent its transformation into a more aggressive form of the disease-squamous cell carcinoma.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...