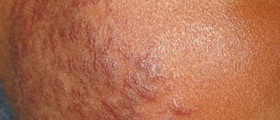
Flat brown lesions on the skin which don’t turn darker after exposure to the sun are known as lentigines. Lentigo lesion is usually 5 to 20mm large and can be of irregular shape. They affect young people who spend a lot of time in the sun, especially their shoulders. Lentigines may also appear in elderly, on the areas of the body exposed to the sun. In older people, lentigines are seen on the upper part of the hands, on the face, neck and also on the forearms.
These skin lesions are different than the freckles or ephelides, because these change the color on the sun. Doctors and patients should differentiate this condition from actinic keratosis, seborrhoeic keratosis and xeroderma pigmentosum. Melanoma and lentigo maligna are malignant changes of the skin (malignant skin lesions).
Types of Lentigo
There are numerous types of lentigo and diseases associated with this condition.
Agminated lentiginosis affects children after birth or develop in early childhood and may be connected with different childhood diseases.
Genital lentigo may appear in both men and woman, affecting glands, shaft or corona (in men) or genital mucosa in women.
Ink-spot lentigo usually appears solitary, after exposure to the sun. Sometimes, people may mistake these for melanomas, although these changes are benign.
Lentigens profuse affect arms, legs and genitalia without any trigger factor or abnormality associated with this condition.
Lentigo simplex is actually the most common of lentigines and usually affects the kids. It is not caused by exposure to the sun.
PUVA lentigo occurs in people after PUVA psoriasis treatment and persists for several months or even several years.
Radiation lentigo are commonly seen in people exposed to excess radiation (such was Chernobyl).
Solar lentigo, as the name suggests, appears due to sun exposure. It appears in 30 to 50 year old people, but it can affect younger generation as well.
Sun-bed lentigo is seen after excess exposure or after long-term use of sun beds. They usually appear on the arms and legs.
Diseases that might be associated with lentigo involve: LEOPARD lentigines, Peutz-Jeghers and Laugier-Hunziker syndromes, as well as myxoma syndromes such as: LAMB - lentigines, NAME and Carney syndrome.
Diagnosis and Treatment
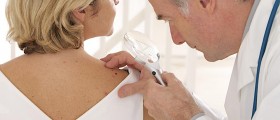
When you are not sure what is happening to your skin, it is best to visit the doctor. He or she will be able to biopsy the lesion and determine whether the problem is benign or malignant.
Local chemical peel or use of lasers (ruby, Q0switched or ND-YAG) can be efficient for lentigines. Some lesions on the face can be improved by freezing, while avoidance of the sun and the use of sunblock creams and lotions can prevent development of new lentigines. Doctors also advise keeping the shirt on during the exposure to the sun.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...