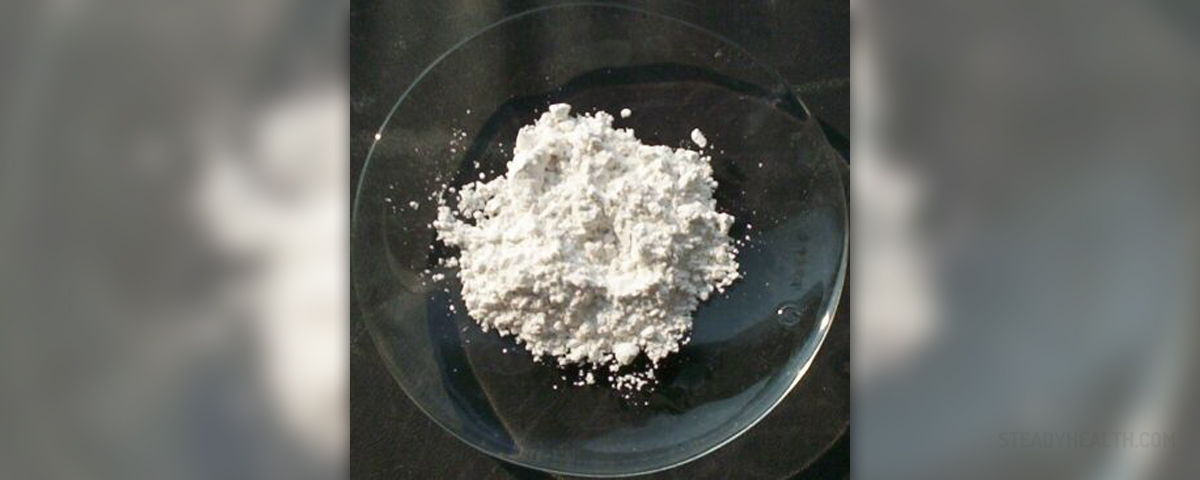

Information on Calcium Sulfate
Calcium Sulfate is a certain type of industrial andlaboratory chemical which is used for numerous different types of purposes. Itis commonly used as a coagulant or as a desiccant. When it is in its naturally occurringstate it is a white crystalline translucent rock. It may appear pink or bluewhen sold as Drierite because it gets impregnated with cobalt chloride. The dehydrateoccurs in its natural form as gypsum while the hemihydrates is commonlyreferred to as plaster of Paris. Alpha and beta hemihydrates may also bedistinguished, depending on the method of calcination used on the calciumsulfate dihydrate, and the only thing that makes them different is the size oftheir crystals. The alpha hemihydrates ones form a much stronge superstructurewhen they get mixed with water.
Commercial production and recovery
Calcium sulfate is commonly derived from the naturallyoccurring sources such as anhydrite and gypsum, which are available everywhere aroundthe world in the form of evaporates. The world’s yearly production of naturallyoccurring gypsum is somewhere around 127 million tons. Calcium sulfide may alsobe produced by utilizing numerous different types of processes, butunfortunately, such processes cause the concentration of radioactive elementsin the final product. Calcium phosphate may be treated with calcium sulfuricacid in the production of phosphoric acid so that calcium sulfate canprecipitate.In the process of desulfurization of the flue gas the finely groundlimestone gets injected into exhaust gases, and calcium sulfate is the finalproduct of the oxidation of the stored impure calcium sulfite. Calcium fluoridegets treated with sulfuric acid in the production of hydrogen fluoride so thatcalcium sulfate may precipitate. Calcium sulfate may also be obtained from therefining of zinc and it can also be recovered from scrap drywalls at constructionsites.
Dehydration reactions
Gypsum needs to be heating to a certain degree so that itcan dehydrate partially. This process drives off the better part of water fromits chemical structure. The process ofdehydration is also sometimes referred to as calcinations so that is why thepartially dehydrated mineral also sometimes gets referred to as calcinatedgypsum. When the mineral gets mixed with water at normal temperatures itreverts to the dihydrate form. Gypsum can be cast into various types of shapes.It can also be mixed with different sorts of polymers. The dehydration may beadjusted in order to control the porosity of the material.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...