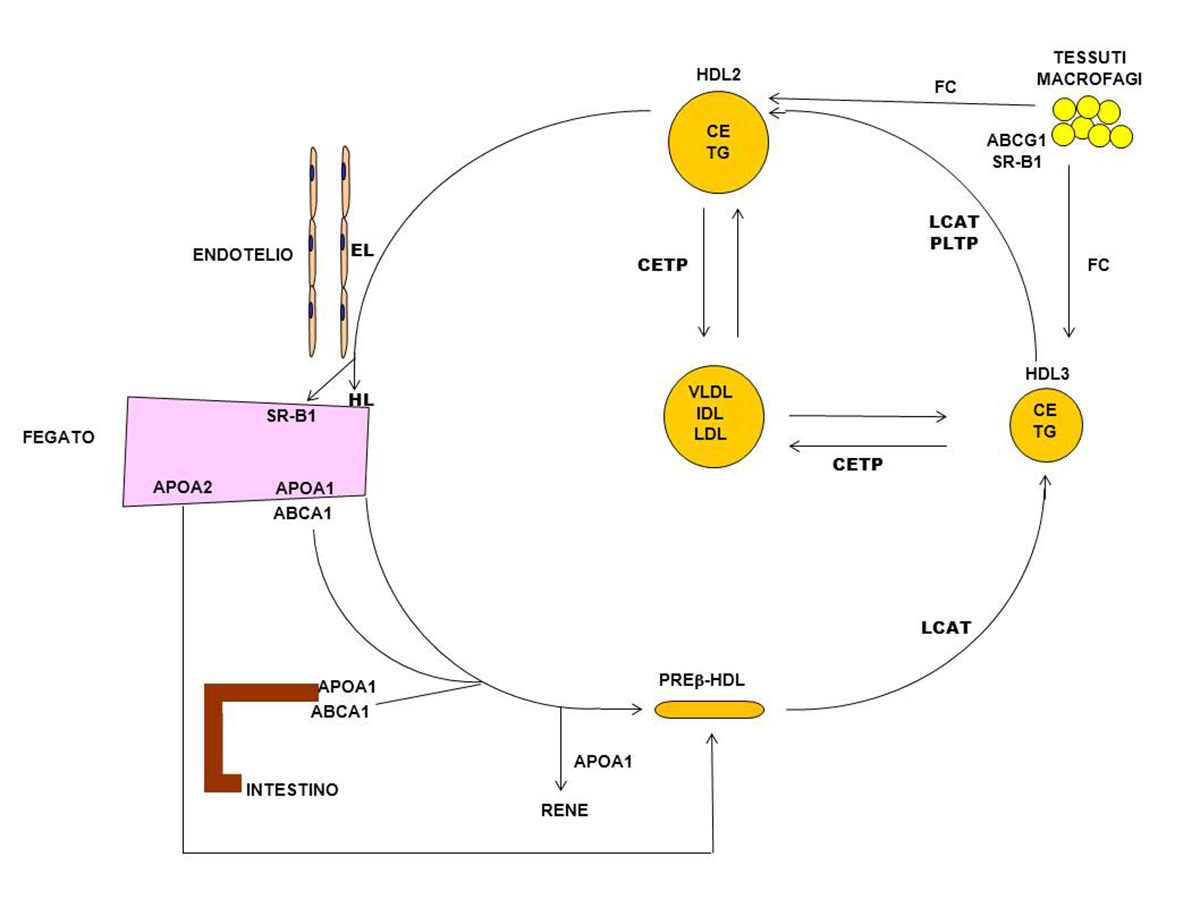
Lecithin has a significant element of VLDL (very low density lipoproteins) which aids the conveyance of fats throughout the body. It is often encountered in milk, cheese, meat, and other kinds of food, however, the largest amounts are contained in soybean.
One of its functions is preventing cell membranes from densifying. It also helps liquids to dissolve in liquids. The human brain and prostate glands also contain lecithin. The main components of lecithin includes cholineinositol and linoleic acid.
Another kind of lecithin, phosphatidyl choline, disperses cholesterol and lipids, keeping cell membranes soundly.
Choline, a B vitamin, helps the integration of proteins and phospholipids in cells. It can be found in lecithin.
Lecithin as a supplement has a beneficial effect on the liver and lipotropic activities. It can also have a positive effects on the cognitive processes and other neurological problems, including Alzheimer's disease and tardive dyskinesia.
Over 40 years ago, Japanese scientists noticed that iodine-lecithin reduces cholesterol.
Ten years after, an experiment conducted by Simons LA et al confirmed that cholesterol can be reduced by administering lecithing orally.
In the 90’s, French scientists proved that overall reduction of HDL-cholesterol due to the administration of hepatic phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. Four years later, they used hypercholesterolemic rabbits to explain the cholesterol-lowering mechanisms by the usage of a dietary soybean lecithin.
Once again, the ability of soy-lecithin to reduce cholesterol has been proven. In one case, a group of scientists from University of Massachusetts Lowell claimed that this process was conducted without lowering HDL-C levels of plasma. Later on, a group of Russian scientists demonstrated that the combination of lecithin and lovastatin yielded enhanced results in the reduction of lipids.
Side effects are commonly the consequence of irregular use from injections.
In cases of over-ingestion it is possible to lose weight or have pain in the abdomen, among other complications resulting from the lecithin.
Phosphatidylcholine (a lecithin-derived phospholipid) injections were administered in regions with high levels of fat to volunteers, and the reduction of fat was evident in the findings.
Cancer mice were given the lecithin-related liposome products intraperitoneally which resulted in a longer survival rate. No other side effects were registered in this case.
It is demonstrated by an experiment conducted on patients with a chronic congenital T-tube that the administration of lecithine can be used in the lipid acyl chain regulation of membranes and bile as well to help treat the condition.

















Your thoughts on this
Loading...