
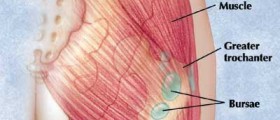
Water on the knee is medically known as knee effusion. It is a medical condition in which, excess fluid accumulates in or around the knee. The condition may develop as a result of trauma, overuse injuries and it can be also associated with certain underlying conditions.
It is normal for certain amount of fluid called synovial fluid to be inside the knee joint. Its function is to lubricate the cartilage and prevent excessive friction and subsequent damage of the knee tissues. In patients suffering from knee effusion the production of synovial fluid is increased and its excess leads to certain symptoms and signs.
Causes of Water on the Knee
In many cases, water on the knee develops due to trauma from an injury of the knee (damage to bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons or meniscus). Overuse injuries are commonly associated with the occurrence of water on the knee. Furthermore, this condition may be a characteristic of other underlying illnesses such as gout, pseudogout, arthritis, infections, kneecap bursitis, cysts and tumors. Some people (obese people as well as athletes) are more susceptible to water on the knee.
Symptoms of Water on the Knee
The most prominent symptom of water on the knee is swelling of the particular area. The affected knee is noticeably larger than the other knee. A patient may also complain about discomfort or pain, in the knee. The very presence of the excess fluid can interfere in the movement of the knee joint and limit the movement of the knee. Water on the knee caused by trauma and injury is also accompanied by bruising of the nearby skin.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Water on the Knee
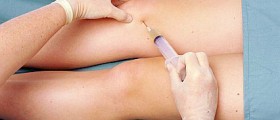
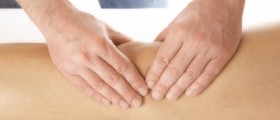
In order to set the diagnosis, a doctor investigates patient's medical history and performs a physical examination and certain tests. A sample of the fluid taken from the knee may be of great help in identifying the actual cause of water on the knee. The presence of bacteria in the sample taken can confirm if there is a bacterial infection and blood indicates traumatic injury. Additional diagnostic tests include X ray of the affected knee, MRI and specific blood test that may point to infection, rheumatoid arthritis, gout or bleeding disorders.
The symptoms tend to lessen with adequate rest (particularly in case of trauma and injury). The knee is supposed to be elevated, in some cases ice packs can be applied and if the pain and inflammation do not subside, patients are prescribed medications (NSAIDs or corticosteroids). If there is too much fluid in the knee symptoms may subside once the doctor performs aspiration and eliminate the excess of fluid. Only if conservative treatment fails to provide with desirable results and depending on the actual cause of water on the knee the doctor may recommend surgery.



-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)


-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...