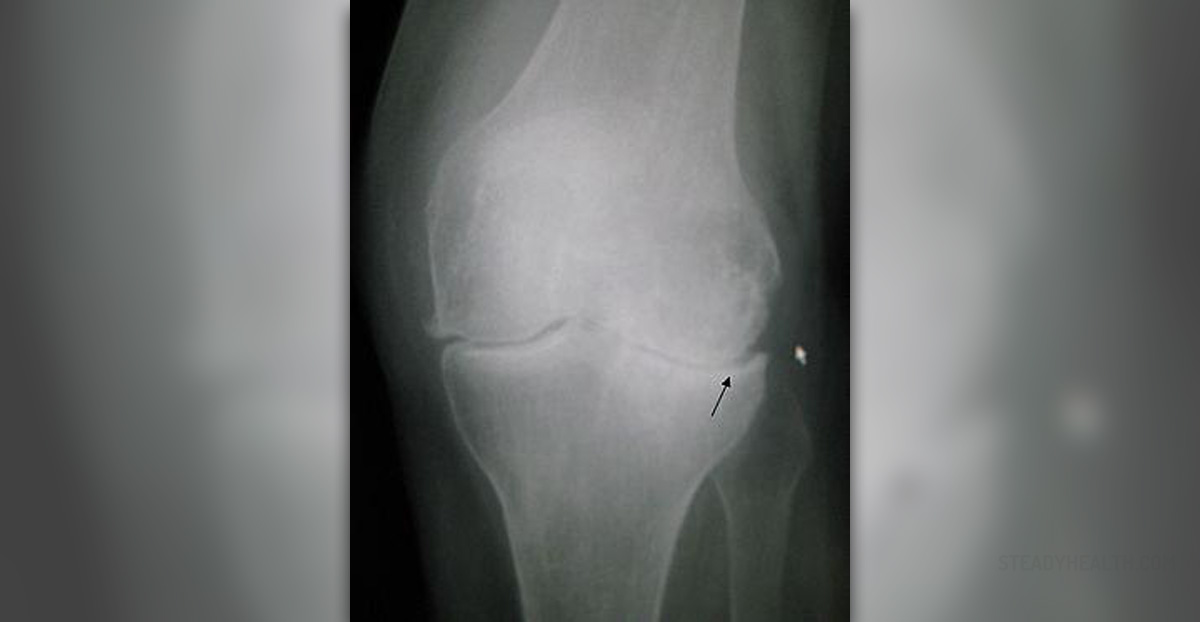
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that leads to wear and tear of different structures of joints. In osteoarthritis of the knee degenerative process affects the knee joint. The condition is frequent among people older than 40 and predominantly affects women.
Causes of Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Cartilage in the knee joint plays a significant role in prevention of damage to the bones that would develop if there was no such structure in the joint. This makes a knee cartilage a powerful cushion. But in patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis cartilage is damaged and the bones that the knee consists of start rubbing against each other. Friction between the bones is responsible for structural damage and it also affects function of the knee.
Degeneration and wear of the knee cartilage develops due to aging or it is a consequence of inflammation. Osteoarthritis of the knee is more frequent among obese people, those with previous trauma or injury to the knee and also affects people with certain congenital defects. Osteoarthritis of the knee can be additionally associated with gout, diabetes or Marfan's syndrome.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Pain is a typical symptom of knee osteoarthritis. It ranges in intensity and while some patients suffer from mild discomfort others have to deal with excruciating knee pain. The condition may also lead to knee effusion (knee swelling). Inflammation of the knee joint is responsible for another symptom of osteoarthritis - stiffness of the affected joint. Many patients may complain about worsening of the symptoms during cold or wet weather.
Treatment for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Damage to the knee cartilage is irreversible so the goal of the treatment is to reduce discomfort and pain as well as other symptoms and signs of the condition.
Pain management includes different pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs. Patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis may benefit from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or they receive corticosteroid injections. COX-2 inhibitors are also highly effective against inflammation of the knee joint. Patients with mild symptoms are prescribed with topical creams or ointments.
Physical therapy for knee osteoarthritis includes specially designed exercises. The goal of such treatment is to provide with pain and spasm relief, reduce stiffness, strengthen the knee muscles, increase the range of motion and flexibility and improve balance.
Obese patients are advised to lose weigh and engage in physical activity such as walking, swimming or water aerobics. Patients with severe damage may require a cane or a walker and surgical treatment is recommended in case of serious damage to the knee tissues.


-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)








Your thoughts on this
Loading...