Types of Uvula Problems
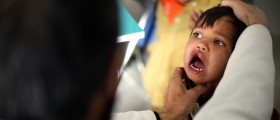
The uvula is the lump of tissue that hangs down in the back of the throat, attached to the end of the soft palate close to the tonsils. It consists of muscle tissue, connective tissue and some racemose glands. The uvula helps the mouth to form spoken words properly by aiding articulation. A fairly sensitive body part, the uvula is at risk for a variety of problems.
Uvulitis is when the uvula swells to three to five times its original size; this can occur due to irritants affecting it, smoking, dehydration, allergies, infection or snoring. The enlarged uvula makes talking and swallowing fairly difficult and can cause the person to feel like they are choking if it grows large enough to touch the throat or tongue.
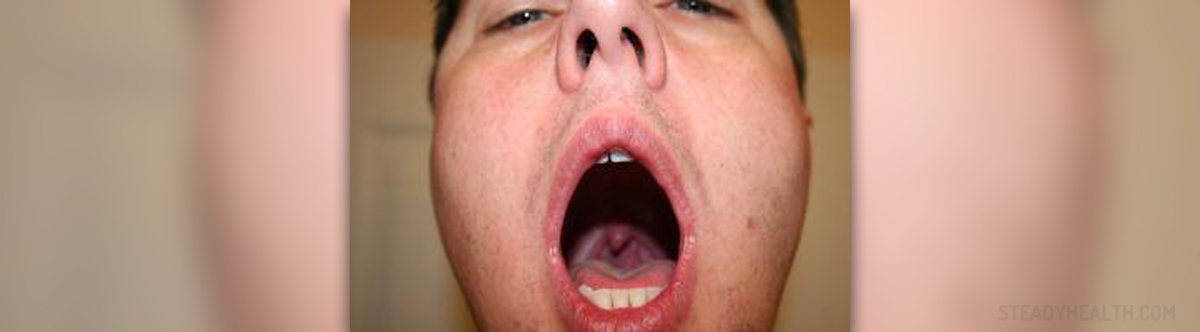
When the uvula is split due to malformation, it typically contains less muscle fibre than an ordinary one. This so-called bifid uvula can lead to problems with the ear and the nasal cavity. While swallowing food, the uvula forces the soft palate to cover the nasal cavity to prevent food from entering it. However, a bifid uvula does not do this properly and can allow food past the palate. This problem typically affects children and babies, but is very rare in adults.
When food enters the nasal cavity due to the uvula not sealing off the nasopharynx correctly while swallowing, it is known as nasal regurgitation. This is usually seen in people with neuromuscular problems like VPI and myositisides.
Some people's uvula simply does not function correctly and does not fully close off the back of the throat. This is called a velopharyngeal insufficiency and inhibits normal speech, since the soft palate needs to close in order to properly pronounce the letters T, P, G, B and D. This problem causes the person to speak in a nasal voice since too much air enters the nasal cavity during speech.
- A 1 year old boy was referred with the history of spasmodic cough since the age of 6 weeks. This distressing cough usually ended in vomiting with variable symptomatic relief. The coughing episodes were mainly observed during the daytime and often precipitated by a semisolid or solid diet. There was no history of cold, temperature, or breathlessness associated with it.
- Apart from this distressing symptom, he was asymptomatic and thriving well. His growth was appropriate for his age. He was born by emergency lower segment caesarean section with birth weight of 3200 g. His neonatal period was uneventful. He was fully immunised and had not come in contact with whooping cough.
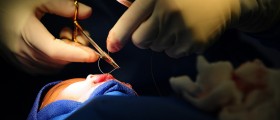
- The patient’s father is from Morocco and as a young child he underwent uvulectomy. This is a common ritual performed for all babies in Morocco. There was no other relevant family history.
- The uvula is an appendage of soft palate and is formed by the fusion of the two halves of the soft palate. It is an important structure in producing a tight seal in the pharynx during speech and feeding. An elongated uvula can flop down and touch various structures in the upper airway including the posterior pharyngeal wall, epiglottis, and vocal cords. Irritation of these structures can lead to chronic cough.
- There are case reports of the uvula causing apnoea due to irritation of the epiglottis or vocal cords. Uvulectomy led to relief from these symptoms. In Africa, especially in the Muslim community, uvulectomy is an ancient ritual/tradition and is as common as circumcision. There are various case reports and commentaries from the literature in 1970–80. Uvulectomies are normally performed by traditional healers with indifferent results.
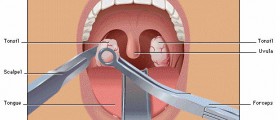
Sleep apnea is a problem whereby the uvula is too long and can interrupt the flow of air while breathing because there is not enough space in the velopharynx for the air to pass freely. This can cause snoring or excessively heavy breathing while sleeping. To correct this problem, a portion of the uvula can be surgically removed to allow better air flow.
Treatment
Some uvula-related problems are caused by dehydration, especially uvulitis. Drink more water and fruit juice in this case to help relieve swelling of the uvula. If the problem stems from an infection, rinsing the mouth with salt water can help fight the infection. Try to avoid coughing, as it can aggravate uvula irritation. Foods containing a lot of salt or foods rich in fats and carbohydrates, like pasta, potatoes, fried meat and rice, can cause some uvula problems, so limit the intake of these.










-And-Breathing-Problems_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...