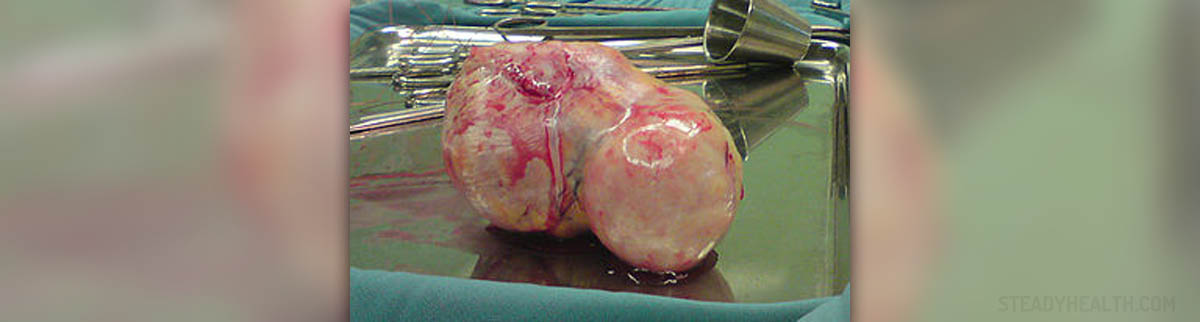
Uterine fibroids are typically non-cancerous and can grow in and around the uterus, leading to distortion of shape and size. Fibroids normally range in size from a few centimeters and can grow to be 15 centimeters or more. Usually present in clusters, if one is detected during a pelvic examination chances are there will be more. Typically, between 50-80% of all women will have at least one during their lifetime and approximately 20% will endure problems related to the condition. There are three different types of fibroid tumors and classification depends upon the location within the uterus.
An Intramural fibroid grows inside the uterine wall and are the most common type, subserosal fibroids grow on the outside of the uterus and can become larger and may extend outward on a stalk. Submucosal fibroids grow outside the uterus and account for and approximately 5% of all types of fibroids. Uterine fibroids can happen to a female of any age, but women between the ages of 20-50 are more likely to develop larger fibroids. Though fibroids tend to grow in size during pregnancy, it is not likely to cause any problems. Uterine fibroids and pregnancy complications can include heavy bleeding, pain in the pelvis, and constipation, though most fibroids do not cause problems with pregnancy.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy complications while rare, can lead to an increased risk of premature labor and miscarriage. Occasionally additional complications can happen if the fibroids become very large and may include; obstructed labor, fetal malpresentation, postpartum hemorrhaging, stalled labor or cesarean section. During pregnancy, a woman needs to seek treatment for uterine fibroids and a healthcare provider will provide instructions and advice which will protect the health to the female and the developing infant.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/fibroids/complications/
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000914.htm
- Photo courtesy of SnowBink by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Uterine_fibroid_02.jpg












Your thoughts on this
Loading...