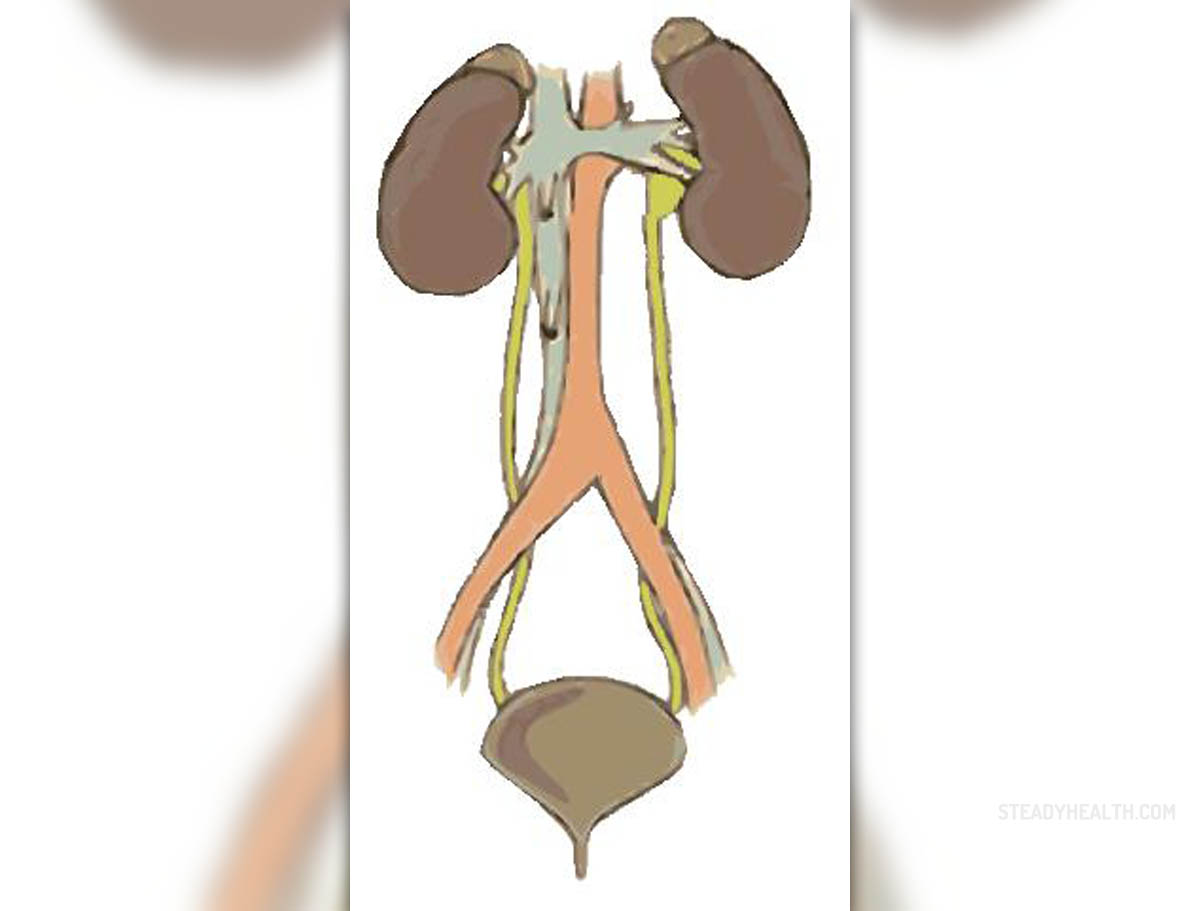
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is relatively common health issue affecting both males and females. It develops as a result of uncontrollable multiplication of bacteria in certain parts of the urinary tract, predominantly the bladder and the urethra. However, the infection may initially affect these organs and soon spread to the kidneys (pyelonephritis).
Even though anatomical structures of female urinary tract make women more susceptible to infections of this type, it is essential not to neglect UTIs in men since bacteria practically have the same detrimental effects on the affected organ/organs.
Why is UTI Very Uncomfortable?
As it has already been mentioned UTI occurs once certain parts of the urinary tract get colonized by bacteria, microorganisms that are basically not found in urine. Urine is under normal circumstances sterile and has specifically determined amount of certain chemical compounds. Now, when bacteria enter the urinary tract, and start to multiply, the very presence of these microorganisms or their toxins irritates the surface of the affected organ and triggers inflammation. As we all know inflammation of any kind is not pleasant at all. It is characterized by swelling, unpleasant sensations such as discomfort or pain and many additional health problems.
In case of urinary tract infections inflammation predominantly affects the bladder and the urethra. Inflammation of these organs is typically accompanied by frequent urination (which is rather painful) and an urge to urinate even though the bladder is actually empty, pain or discomfort in the lower portion of the abdomen and there are obvious changes in the urine's appearance. Namely, it becomes cloudy, may contain blood which makes it red and is also of rather unpleasant odor. If the patient additionally has fever, it is highly likely that infection has spread to the kidneys and triggered their inflammation as well.
Being uncomfortable is not the greatest problem when it comes to urinary tract infections. These infections require aggressive treatment with antibiotics which are capable of complete eradication of microorganisms preventing infection recurrence.
As far as causes of UTIs in men are concerned, they are similar to causes of UTIs in women with a few exceptions. First of all, infections of this type are frequent if the urinary tract is abnormal i.e. if there is anatomical/functional abnormality of some parts of this organ system. For example, in patients suffering from vesicourinary reflux disease, urine regurgitates to the kidneys because it is simply cannot pass down into the bladder due to stenosis of the ureters. Such regurgitation leads to severe kidney damage and makes them prone to infections. Furthermore, functional abnormalities are reported in case there is damage to nerves innervating the bladder which is often seen in people suffering from a variety of conditions affecting the brain, spinal cord and nerves. The bladder may not be able to empty properly. As a consequence, urine accumulates and as such represents a fertile ground for bacterial infections.
UTIs are also closely connected with a blockage in the urinary tract. This basically occurs if there are kidney/bladder stones present or a person is suffering from a tumor of the bladder, urethra etc.
More specific causes of UTIs in men are prostate problems and the absence of circumcision. In men who are dealing with prostatitis (especially the chronic form of the disease) there is higher risk of developing UTI. Similarly, in uncircumcised men excess of foreskin allows bacteria to accumulate and easily enter the urinary tract triggering infections.
Finally, as it is the case with women, immunocompromised men are more susceptible to UTIs compared to men with preserved immunity. This is the reason why men suffering from HIV or diabetes are frequently affected by UTIs and are also prone to disease recurrence.
Does UTI Affect Men more than Women?
Urinary tract infections are definitely more frequent among women. This fact particularly refers to women in adolescence and childbearing years. It is estimated that the condition is reported in women 30 times more than in men. Such discrepancy of approximately the same value is reported in many countries around the world.
It is easy to understand why UTIs are more reported in women. When we take male and female urinary tract into consideration and compare the two, we will get familiar with the fact that the urethra in men is 4 times longer than in women. This anatomical characteristic prevents men from contracting bacteria easily as it is the case with women. What is more, women must realize that wiping from back to front after using the toilet allows harmful bacteria to be introduced into the urinary tract much easily. Because of that, women must be taught how to wipe properly and to learn and maintain impeccable hygiene of their genitalia.
Additionally, incidence of UTIs is higher in men over the age of 50, when they commonly suffer from enlarged prostate, prostatism both of which are blamed for secondary urinary tract infections.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...