The urinary tract is the system that serves for the disposal of liquid waste from the human body. Women have shorter urinary tracts and are more likely to contract bacteria that cause urinary tract infections, or UTI, than men. More than 50 percent of women have had an UTI at least once in their lives.
As a disease, a UTI is not dangerous or too serious, as it can be easily treated with antibiotics, but it can be very uncomfortable and painful.
Among the causes of urinary tract infections, is bacteria from feces that lives on the skin in the area of the rectum and vagina. They can spread and penetrate the urinary tract through the urethra (a tube that leads from the bladder to the outside of the body). From there, the bacteria moves upwards and causes infection of the bladder and other parts of the urinary tract.
Another common cause of UTI is sexual intercourse. During intercourse, the bacteria in the vaginal area penetrates the urinary tract aided by the motion. Women who engage in sexual intercourse more often and with different partners are more likely to get an infection of the bladder or urinary tract than ones who are celibate or monogamous. There are even some women who get an infection after each time intercourse is performed.
Waiting too long to urinate can cause urinary tract infection as well. The bladder is a muscle that stretches as it fills with liquid and contracts as it empties. Waiting too long overstretches and weakens the muscle and the bladder retains some urine even after urination. The urine left inside can cause infection.
Other factors include pregnancy, menopause, diabetes and history of urinary infections in childhood.
The symptoms of a urinary infection are hard to miss. There is a strong urge to urinate even though previous urination occurred shortly before and there might be just a little urine exiting the body. The urine can contain traces of blood and it can be painful. There may also be some pain in the lower abdomen and lower back.
If the infection has spread to the kidneys, the symptoms will include back pain, fever, nausea, along with the symptoms of UTI mentioned above.
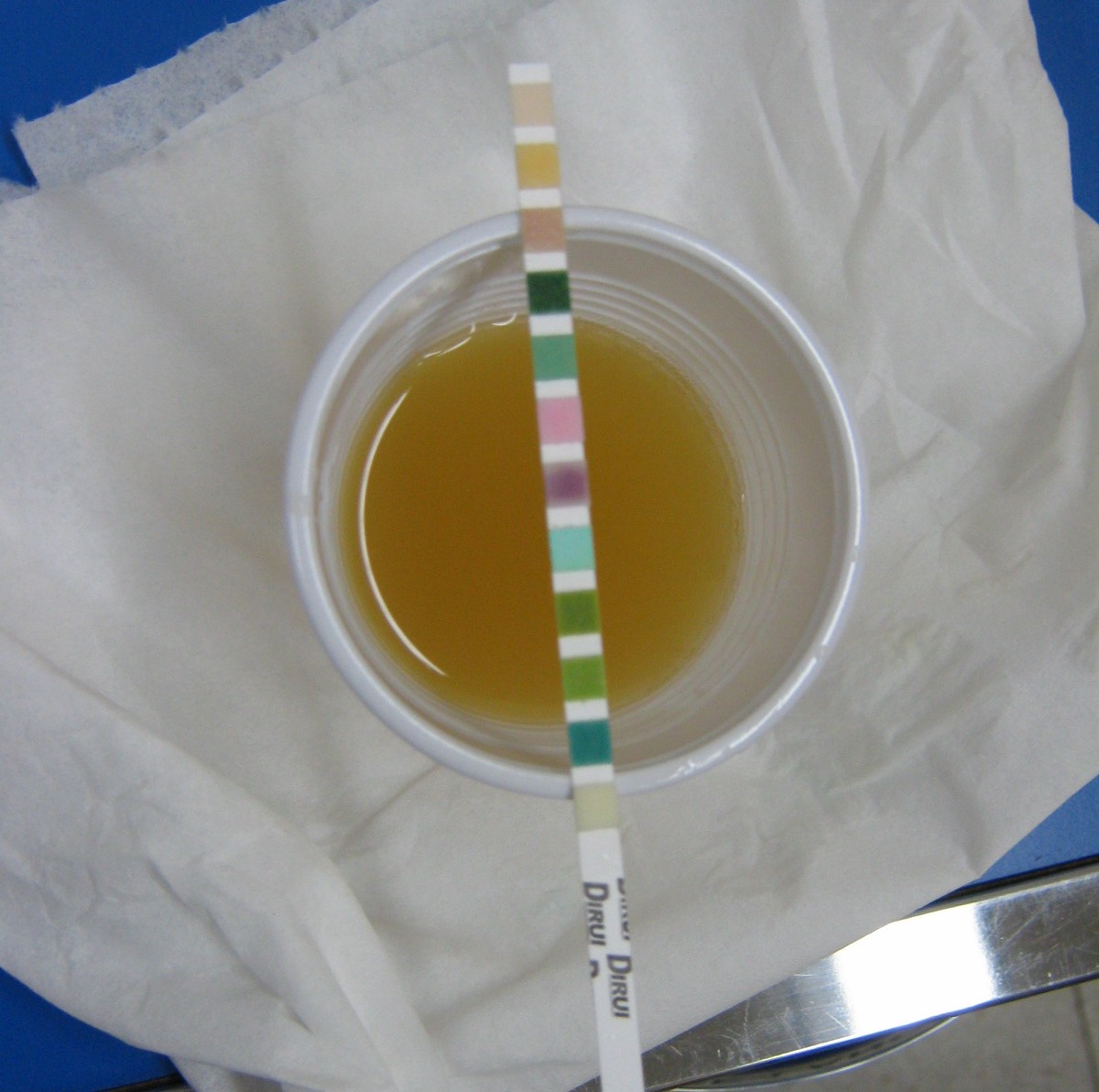
The diagnosis of a UTI requires examination of a urine sample with a microscope. Sometimes the diagnosis requires a pelvic exam as well.
The usual treatment for urinary tract infections are antibiotics. They must be taken as prescribed by a doctor. The symptoms may go away as soon as the treatments start, but it is important to take the whole quantity prescribed because the infection might still be present and it might come back shortly after therapy.
Urinary tract infections can be prevented with simple rules of personal hygiene.
The area should be washed at least once a day and every time after sex. It is also recommended to urinate after sex to expel the bacteria that might be present in the urethra.Wiping should be done from front to back. If there is an urge to urinate, it should not be delayed.
Plenty of fluids, especially water, help flush out the bacteria from the urinary tract. Panties should have a cotton crotch in order to allow dry. Moisture is the best environment for the bacteria to breed. Vitamin C and cranberries are said to help prevent urinary tract infections.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...