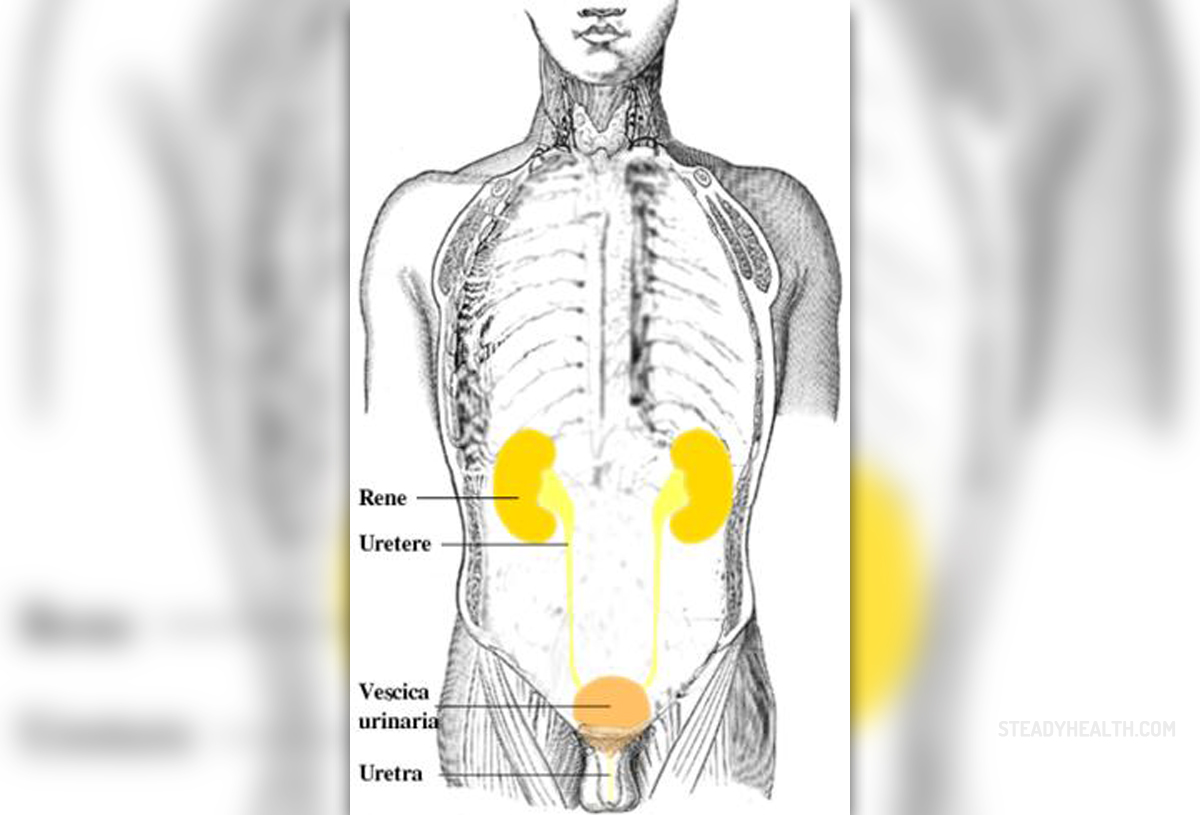
Overview of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Recurrent urinary tract infection does not have a concrete definition, but rather a tentative one which postulates that any individual who experiences urinary tract problems that have to be treated medically twice within a 6 month period, or 3 times within a 1 year’s time suffers from recurrent urinary tract infection. Such infections are primarily bacterial in nature and up to 95 percent of all urinary tract infections are caused by Escherichia coli. There are other types of bacteria, such as Proteus mirabilis and straphylococcus saprophytics, but those are less common. In addition, recurrent urinary tract infections are far more prevalent in women than men. For instance, 1 in every 3 women will suffer from UTI in her lifetime while only 1 in 20 men are likely to be affected. Across all age groups of men the UTIs are rarely observed. Further, most repeated infections are due to the fact that the bacteria were never stopped properly. Infants and elderly people, both men and women, are more prone to recurrent urinary tract infections than their teenage or middle aged counterparts. When it comes to risk factors, there have been genes identified which predispose certain individuals to UTIs while at the same time diabetes is another factor with a strong contribution to the syndrome. When it comes to gender specific risk factors, some of them differ between men and women. If a woman has an underlying immune system problem she is more likely to suffer from UTIs than a woman who does not. Various types of birth control methods, such as spermicide-coated condoms or diaphragms put a woman at more risk for contracting the syndrome. Underlying urinary tract problems, such as not emptying the bladder completely or having had surgery in the area are also elements which predispose women to problems. Lastly, sexual intercourse is one of the leading risk factors for UTIs in women. When it comes to men, anal sexual intercourse puts them at risk, and so does an underlying immune system disease. Similarly to women, any problems in the area, surgeries, or incomplete bladder emptying increase the risk of UTIs. When it comes to children, kidney problems, immune system impairment, sexual abuse, underlying urinary tract problems as well as constipation all increase the possibility that a child might suffer from UTIs.
How to Know if You Have Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Signs and symptoms of the urinary tract infections include discomfort in the abdomen area, frequent urination, and having to urinate suddenly and urgently. In addition, the urine is usually darker, in some cases there is blood in it visible to the naked eye, and it has a stronger smell than usual. When it comes to the elderly, they may get high body temperature as well. Once these symptoms appear and do not go away naturally after a few days it is recommended that the individual seeks medical attention. Diagnosing urinary tract infections is a fairly simple task which includes a culture test of the bacteria and in some cases a ultrasound. In instances in which the infection threatens to persist and leave numerous adverse consequences scanning is recommended in order to get a better idea of kidney and urinary tract functionality.
Is it Manageable?
Urinary tract infections can be very persistent and once commenced difficult to get rid of. Many individuals experience relapse as a result. A recurring infection should be treated with antimicrobials for the first few days, but if there are no results a medical care provider should be consulted. The medical care provider will prescribe a course of antibiotics usually a few weeks long. In addition to the medications, drinking cranberry juice or tea is highly beneficial for the urinary tract. In case the recurring urinary tract infection is related to sexual intercourse it is advised that women empty bladders before and after, change their methods of birth control or begin using a lubricant. Some experts advise that if an individual suffers from 3 recurrences per year that an antibiotic should be taken 2 hours after each intercourse.
Research Results
There have been numerous research articles attempting to explore urinary tract infections, their symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, and there is much useful information to be obtained. For instance, trimeothoprim compared to amoxicillin is more powerful in eliminating bacteria and therefore less likely to lead to longer courses of antibiotics. Other commonly used antibiotics were just as effective as trimeothoprim. Interestingly, individuals who take effective antibiotics for 3 days reach the same results as those who take them for 5 or 7 days. When it comes to UTIs in men they are often the symptom of other conditions, such as prostate and other related problems. Just as in women, UTIs in men are treated with a week or more of antibiotics, but a medical care professional should be consulted about the treatment of a possible underlying issue which is causing the UTIs in the first place.

















Your thoughts on this
Loading...