Urinary tract infections or UTIs, are the second most common infections that affect the human body. They are responsible for about 8.3 million visits to the doctor’s office each year. They are more likely to affect women than men, probably because female urethra is shorter and bacteria are more likely to penetrate the urinary tract.
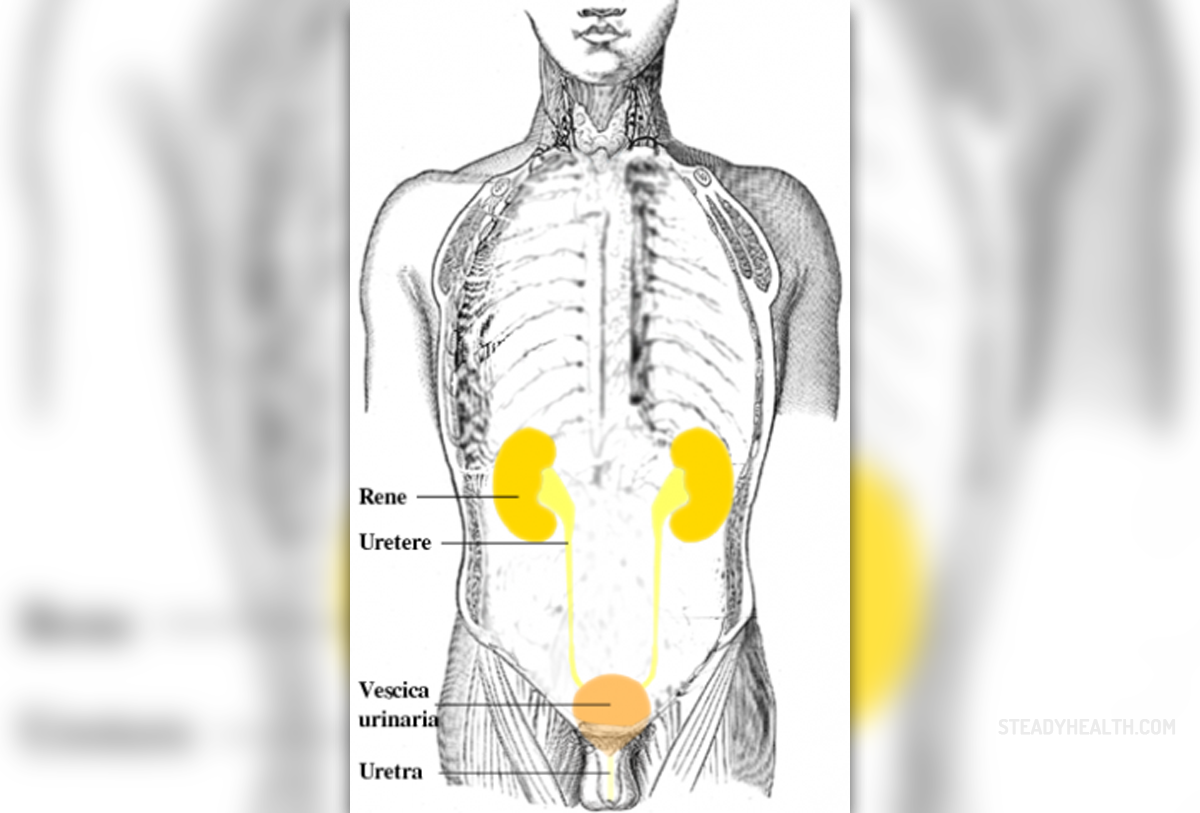
The urinary tract
The urinary tract or urinary system is comprised of urethra, kidneys, bladder and ureters. Its function is to produce, store and eliminate urine. The key elements in this system are kidneys, organs that remove excess fluids and waste from blood through urine, maintain the balance of electrolytes and produce a hormone responsible for the formation of red blood cells.
Ureters carry the urine to the bladder, which stores the urine until it is emptied out through the urethra.
Causes of urinary tract infections
In normal conditions, human urine is sterile and it does not contain bacteria, viruses or fungi. Therefore, the infection cannot be caused by the urine itself. However, certain microorganisms, especially the bacteria that live in the colon, can cling to the opening of the urethra and penetrate the system. If the bacteria multiply, they cause an infection.
The infection of the urethra is called urethritis. If the bacteria move on and reach the bladder, where they continue to multiply, the infection is called cystitis. If this infection is not stopped with proper treatment, it will spread further and affect the kidneys.
Risk factors for urinary tract infections
As it is mentioned above, women are more prone to UTIs than men but there are other factors that increase the risk of getting a UTI too. For example, any abnormality in the system can increase the risk, for example a kidney stone. Enlargement of the prostate also affects the urine flow, which often leads to infection. Catheters are also known for increasing the risk.
People who have diabetes often suffer from UTI. In adult women, the risk of UTI increases with age. Also, the infection is in women often triggered by the sexual intercourse. Infants born with abnormalities in the urinary system are also at risk.
Symptoms of urinary tract infections
The symptoms of UTI depend on the severity of the infection. Sometimes the infection can be asymptomatic, but in most cases a person experiences at least one of the symptoms.
The symptoms may include frequent urge to urinate, burning or stinging while urinating, pain or cramping in the lower abdomen or in the lower back, cloudy or smelly urine, possibly with traces of blood, sometimes fever and general fatigue.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...