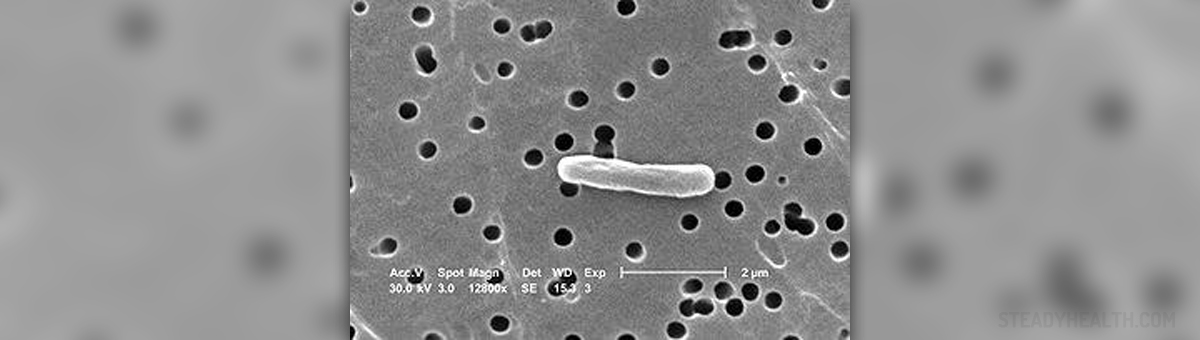
Urine is under normal circumstances sterile fluid which is eliminated from the body on a regular basis. It contains many waste products and all the substances from the body which are present in abundant quantities. The term bacteriuria refers to the presence of bacteria in the urine, which is not normal. Furthermore, urinary tract infection suggests the presence of certain symptoms and signs because of bacteriuria.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) can be divided into lower and upper UTI. The first one affects the bladder while the second one additionally affects the kidneys. UTI can be recurrent, when it repeats from time to time. How many times UTI will reoccur basically depends on age and sex. Uncomplicated UTI is infection characterized by the presence of unusual pathogen in people with a normal urinary tract and preserved kidney function. Complicated UTI, on the other hand, develops in individuals in whom there are anatomical, functional or pharmacological factors which contribute to persistent infection, cause recurrent infections and infection which is hard to eradicate.
Pathogenesis of UTI
There are several microorganisms which may cause UTI. These include Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Proteus mirabilis. Furthermore, Klebsiella spp., Proteus vulgaris as well as Pseudomonas spp. urinary infections generally affect people who have underlying pathology of repeated UTIs, those who are immunodeficient and patients who are catheterized.
UTIs are less common among men at all ages. Also, if there is any abnormality in the renal tract, infections are more likely to occur. Frequent use of antibiotics can be associated with changes of the vaginal flora and may initiate colonization of the genital tract with E.coli. This is a risk factor for further UTI infections. The risk for developing UTI also increases in individuals who have recently had sexual activity, those with a new sexual partner, people suffering from diabetes, catheterized and institutionalized patients as well as pregnant women.Treatment for UTI
General measures all patients suffering from UTI must apply include cessation of spermicide use, discontinuation of sexual intercourse until infection is eradicated and intake of plenty of fluids. Cranberry juice has been proven to be efficient when it comes to elimination of microorganisms from the urinary tract.
The most efficient means for UTI are antibiotics. Trimethoprim remains the drug of first choice in case of empirical treatment and uncomplicated UTIs. However, confirmation of Escherichia coli is a reason to opt only for antibiotics which have been shown by antibiogram to be effective against the particular strain. Depending on the severity of UTI doctors determine for how long antibiotics are supposed to be taken and sometimes even opt for a combination of two or even three antibiotics. They are taken subsequently.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...