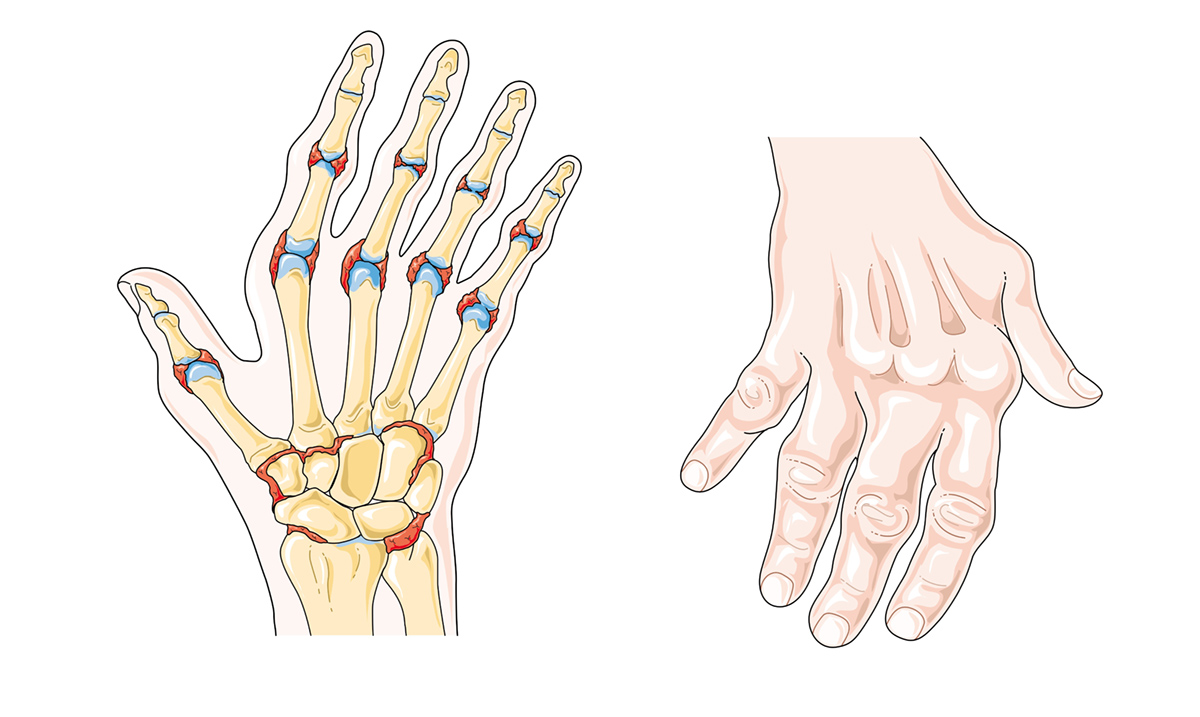
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, progressive, inflammatory rheumatic disease which cause is still not sufficiently known. Given that it attacks connective tissue of the whole body, this disease is classified as systematic disease of the connective tissue. The main characteristics of this disease are reducing the cellular immune system, increasing the number of B lymphocytes and hypergammaglobulinemia.Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common disease among rheumatoid inflammatory diseases. The frequency of this disease in the population is about 0.5%. The disease develops between the fourth and sixth decades of life in most patients. Rheumatoid arthritis affects women two to three times more often than men in the generative period, but with age, this ratio decreases.
Causes
Cause of rheumatoid arthritis is still unknown, although considerable progress has been made in understanding the genesis of this disease. It is assumed that microorganisms (bacteria, viruses) are triggers of the disease. Also, autoimmune disorders in the body are among the causes of disease. Besides that, the genetic factors have a significant role in the emergence of rheumatoid arthritis.Symptoms
There are non-specific signs, before the onset of symptoms, such as the presence of weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, irritability, depression, increased sweating, cold and wet hands and feet.There is an occasional pain in the muscles, especially in the shoulders, and stiffness of hand and wrist joints with no visible changes in the early stage of the disease. After a while there is a spindle-shaped swelling of a small peripheral wrist or foot joint. The swelling is painfully sensitive. Morning stiffness, pain, swelling and limited mobility accompanied with other deformations are gradually increasing in the further course of the illness. In addition to joints, this disease affects the other tissues and organs and is manifested in the appearance of rheumatoid lumps, anemia and sores on the skin.
Physicians have defined several characteristic criteria for the last three weeks of illness, and they are: morning stiffness pain and sensitivity while moving joint swelling subcutaneous nodules accelerated sedimentation positive rheumatoid factor uveitis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is easily set when the characteristic criteria are determined by the symptoms in the last three weeks of illness. The duration of joint symptoms and signs is 6 weeks. Laboratory analyses confirm the presence of anemia, increase in white blood cell count, platelet reduction and accelerated sedimentation. Rheumatoid factor is in the serum. There is also an increase of IgM, IgG and IgA. X-ray findings depend on the stage of the disease.Treatment
The disease is chronic and requires a long treatment, but, due to unknown etiology, there is no adequate drug which would achieve a curing. The treatment is mainly based on eliminating the symptoms and reducing the inflammatory processes in the body. General measures include rest and immobilization of the most affected joints.As for medications, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used, but a short-term treatment with corticosteroids can be applied in certain phases of the disease.
The modern concept of treatment represents increasing use of gold salts, which provide long-term prophylaxis of worsening disease. Treatment plan is being implemented in accordance with the standards of reference rheumatological institution.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...