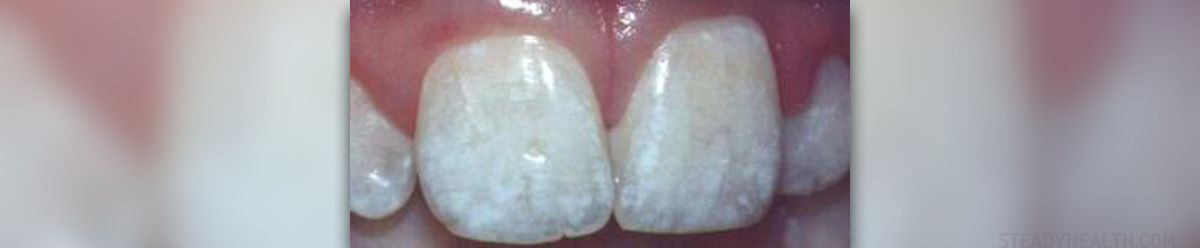
Tooth resorption is a condition in which parts of the teeth are destroyed which affects dental health in general. The condition represents odd body's defense mechanisms which eventually attack the body's own cells. The destruction occurs when the immune system decides that the affected tooth is a threat to the body and is necessary for it to be destroyed. Tooth resorption must be treated timely and if neglected may lead to loss of the affected tooth. The very process of destruction involves interaction among many cells including inflammatory cells, resorbing cells and hard tissue structures. Resorption is eventually achieved with the assistance of osteoblasts and odontoclasts.
There are two types of tooth resorption, internal tooth resorption and external tooth resorption. In external tooth resorption the process starts from the outside of the affected tooth while internal resorption first affects the root and root canal. In external resorption the damage first affects the external surface of the tooth. This type of tooth resorption can be further classified into cervical resorption in which the process may or may not affect a vital pulp and external apical root resorption.
Causes of Tooth Resorption
Generally, tooth resorption is triggered by pressure caused by an adjacent tooth. Even pressure from heavy orthodontic devices can initialize the resorption. Furthermore, bacteria can be triggers of the resorption process. This is typical for people who do not maintain proper oral hygiene. Once the infection or inflammation has started and in case it is left untreated it is an excellent stimulator of tooth resorption.
Furthermore, trauma, direct blow or injury of the nearby tissues may be associated with tooth resorption. This process is considered normal in children if it affects primary teeth. Primary teeth are normally replaced with the adult teeth. So only if the adult teeth are affected by the process of resorption there is a reason for one to be concerned. And finally, tooth resorption may be associated with grinding teeth and tumors or cysts that are hidden beneath the gum line.
Treatment for Tooth Resorption
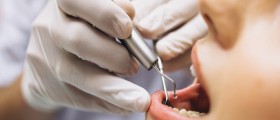
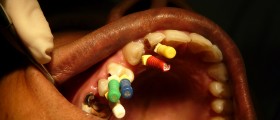
Treatment for tooth resorption depends on the underlying cause of the resorption. If one feels that a tooth has become loose or even wobbly he/ she is recommended to visit a dentist as soon as possible. Internal tooth resorption is generally treated with root canal treatment. This procedure includes removal of the damaged tissue from the pulp. The empty cavity is filled and the tooth is sealed and crowned. Only in case of serious damage the affected tooth must be extracted. It can be later replaced with a dental implant.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...